If you keep up with technology and science news — even from a distance — there’s a chance you’ve heard of Mixed Reality (MR). But what’s it? How does it work? And why does it matter?
Let’s explore the answers.
Understand the Reality-Virtuality Continuum
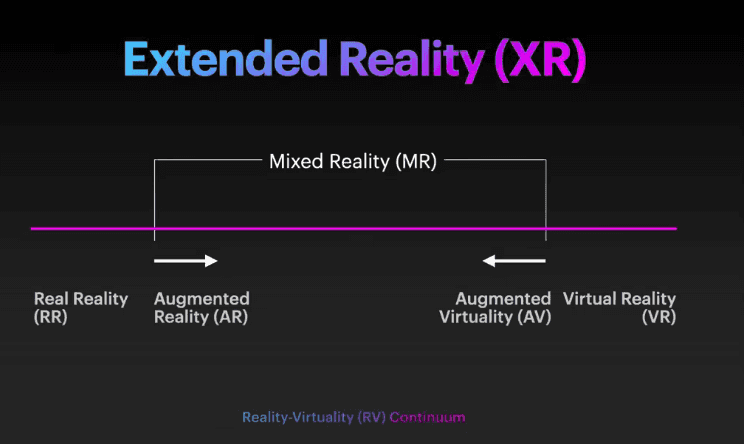
The reality-virtuality continuum illustrates how reality goes from real to virtual. At different points in that transition, real and virtual elements have different degrees of interaction.
At one extreme of the continuum, you have real reality (RR) — the real world as you know it. And at the other end of it, you have virtual reality (VR). VR creates a simulated environment that engrosses the user’s perceptions, a completely virtual experience with no recourse to the real world. Augmented reality (AR) and augmented virtuality (AV) are somewhere between RR and VR.
AR superimposes sounds, graphics, and other elements to the real world — but the virtual and real worlds remain separate. An observer can experience both real and virtual elements in real-time but can’t make them interact. In theory, AV should superimpose Real Reality on Virtual Reality, but that’s currently not possible as we can’t wholly escape into virtuality yet.
Mixed reality, on the other hand, brings the real and virtual worlds together. In MR, virtuality and actuality interact in real-time. MR enables users to manipulate and communicate with virtual and physical environments or objects through high-level imaging and sensing technologies.
This technology can transform the workplace, with its capacity to apply digital information directly to a worker’s real-life experience. This capability explains why most MR solutions tend to attract businesses and researchers.
Extended reality (XR) is the umbrella term for all the realities as a continuum.
How Does Mixed Reality Work?
Mixed reality brings the physical world and the digital world into one reality. MR is not mixed only in terms of real and virtual experiences; it’s also mixed in terms of the technologies that drive it. These technologies range from handheld devices to entire rooms, and each has practical uses in different disciplines.
Let's take a look.
Head-mounted Display (HMD)

Image credit: Wikimedia commons
An HMD uses a small display optic in front of each eye to directly project an image to a user. This device is worn as part of a helmet or over the head. HMD has many uses, including entertainment, medicine, engineering, gaming, and aviation. Its consumers are mostly in the entertainment market as big technology companies develop HMDs to complement their existing products.
Unfortunately, these head-mounted displays are purely digital as they don’t interact with the physical world. However, a well-known augmented reality HMD works better in enterprise environments. For example, Microsoft’s HoloLens has medical apps that offer doctors real-time insight. In engineering, HoloLens overlays essential information on top of the physical world.
Head-up Display (HUD)

Image credit: Wikimedia commons
The HUD provides information without users looking away from their viewpoint. The transparent device has three elements:
A projector, which overlays the display’s graphics,
The combiner, which is the platform the graphics are projected onto, and
The computer integrates the other components. It also makes all real-time adjustments or calculations.
Pioneer’s Heads-up system was one of the first HUD applications in automotive transport. The driver-side sun visor got replaced with a display that gives the driver instructions on the road.
Since then, manufacturers such as Toyota, BMW, and Audi have added some head-up displays in specific models.
Mobile Devices
Mobile devices no longer have computer-generated interfaces on an LED screen. These days, smartphones and tablets have toolkits for developing augmented reality applications.
Pokémon GO was the first augmented reality mobile game with widespread success. Released in July 2016, it got 800 million downloads. The integration is moving beyond entertainment apps utilizing.
Learn how to create your own Pokémon GO-like game.
Google included AR navigation in its Google Maps update. The new feature overlays directions on streets in front of the user. The tech company also expanded its translate app to overlay translated text on physical writing in 20+ foreign languages.
Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE)
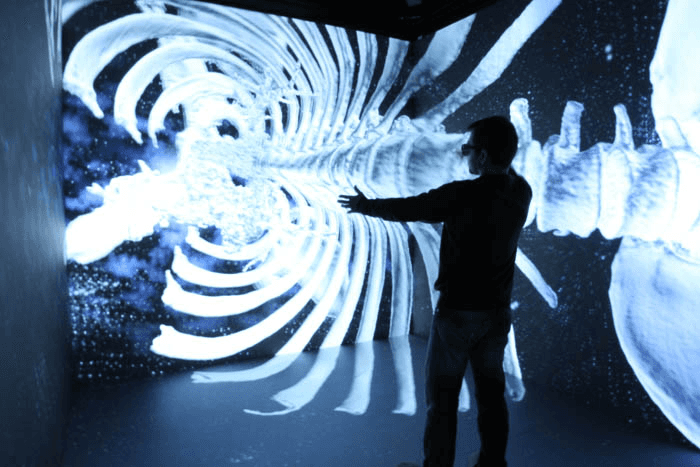

Image credit: phys.org
The Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) is an immersive virtual reality environment where projectors get directed to three to six of a small room’s walls. The small space is typically enclosed in a larger place that must be dark when using the CAVE.
The accompanying surround sound and 3D gives the user a sense of perspective that simulates the physical world. Since its development, CAVE systems have become a testbed for engineers who have developed and tested several prototypes.
Product designers usually test their prototypes before expending resources to manufacture a physical prototype. This process allows for practical testing on untouchable objects like microscopic environments.
After developing the CAVE, the same researchers subsequently released the CAVE2, improving the original CAVE’s shortcomings.
Benefits of Mixed Reality
What makes Mixed Reality great are its benefits. Let’s look at some of them.
Faster Quality Assurance Process
Mixed reality allows on-site teams to verify their work’s quality, lessen errors, and encourage short communication loops within a team. It can also help embed quality assurance in the production process by allowing real-time visual inspection of the assembled product.
For instance, since it adopted Mixed Reality in its production environments, Airbus has announced a decrease in the time required for inspection of A380 fuselage brackets — from three weeks to three days.

Image Credit: Columbia University
Reduction in Maintenance Calls

Organizations that work with outdated manuals are slowly leaving that behind. They’re now using Mixed Reality to limit call out times to maintenance. For example, elevator producer ThyssenKrupp equipped its engineers with HMDs. These displays provide engineers with up-to-date information.
Image Credit: ThyssenKrupp
It also offers a hands-free method to access an expert promptly. Succinctly put, an engineer can call a support line and share the same view with the remote expert on the other end.
This flexibility allows the expert to give instructions and offer solutions without being misunderstood.
Employee Training Advancement
Instead of flipping through several manual pages, employees can receive instructions or attend training sessions via mixed reality. Since sessions can occur on-the-job, there’s a time reduction in creating the training modules and training costs. Read more about successful XR training scenario by checking the INVISTA case study.
For instance, a coaching expert can pre-record a module, and it’ll get stored in a training library for workers.
Curtail Skilled Labour Shortage
A looming skill gap may leave 2.4 million positions vacant between 2018 and 2028. With this looming ahead, employers can act now and retain valuable skills by using remote support via HMDs. As for hiring new talent, employers can integrate new and familiar technologies to a younger demographic. And fill available roles without worrying about under skilled workers.
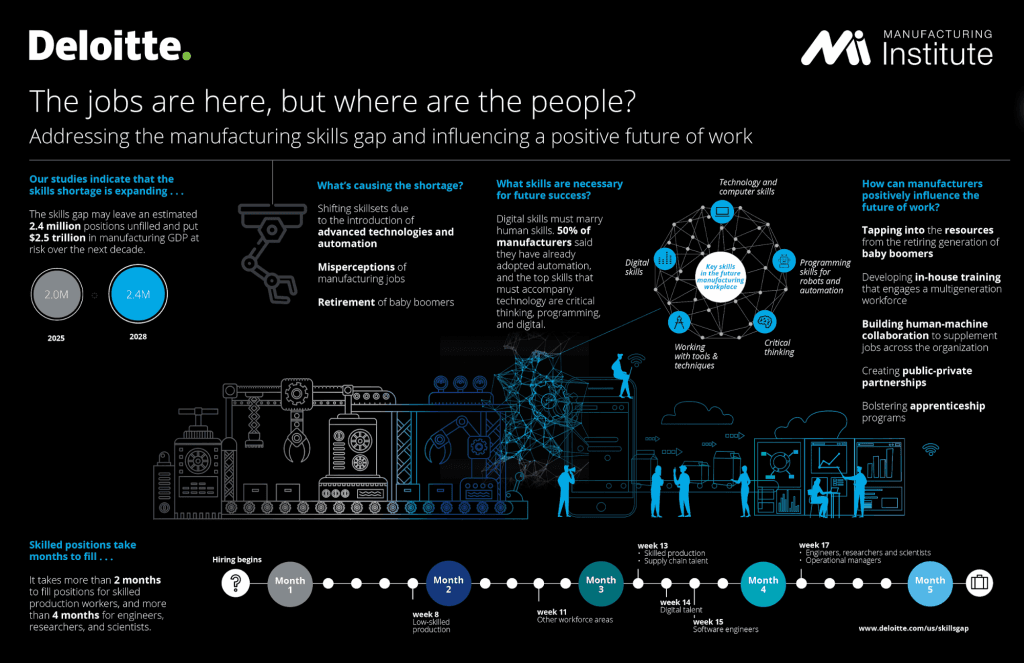
Image Credit: Deloitte
VR, AR, and MR Headsets: Similarities and Differences
While reality technologies — AR, VR, and MR — are gaining momentum, it’s only standard that they have similarities and differences.
Let's start with what's the similarities.
The three technologies leverage features that enhance users’ experience. AR, VR, and MR allow individuals to have sought-after experiences in business, entertainment, and training. Additionally, all three use HMDs, which take users into a virtual world that they can control. Major HMD applications include government, military, and commercial - sports, video gaming, medicine, etc. The head-mounted displays allow for full six-degrees-of-freedom movement - both translation and rotation.
As for their differences.
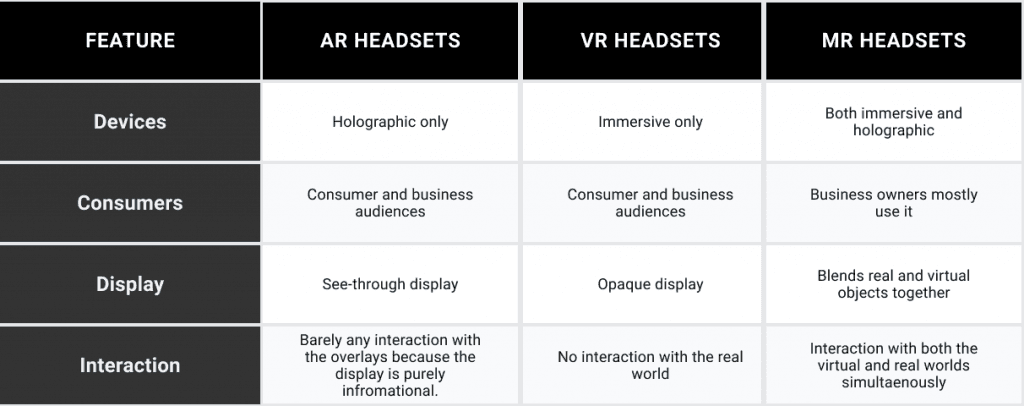
Mixed Reality Headsets
In this section we look at the characteristics of six different mixed reality headsets:
HoloLens 2
Magic Leap
Acer Windows Mixed Reality Headset (WMR)
HP Mixed Reality Headset
Samsung HMD Odyssey and HMD Odyssey+
Varjo XR-1
HoloLens 2
Developed and manufactured by Microsoft, HoloLens 2 is a pair of Mixed Reality smart glasses. On November 7, 2019, Microsoft released HoloLens 2 to succeed the Microsoft HoloLens.
Microsoft improved on HoloLens 2 in three areas:
Ergonomics
Immersiveness
Business friendliness
Let’s explore how the HoloLens 2 stands out.
1. Enterprise High-Tech Experience
Microsoft has years of experience with several high-technology enterprises like:
The US Military: Microsoft manufactured the first version of a custom HoloLens 2 for the Army. The headset comes with thermal imaging, live 3D maps, and data analysis of the wearer’s vitals.
Philips Azurion: Philips Azurion used HoloLens to perform minimally invasive procedures that combine 2D and 3D imaging, allowing physicians to increase their work output and focus.
Nasa: Microsoft supplies Nasa with VR hardware to help assemble the crew capsule, Orion.
2. Market Understanding
Microsoft understands what features will satisfy their clients' needs. As a business solution, the HoloLens 2 implements easy-to-use business applications like:
Remote guidance
Prototyping
Real-time training
The tech company also started an open-source concept, allowing developers to contribute to HoloLens 2’s developments.
3. Upgraded User Experience
HoloLens 2’s user experience (UX) underwent an upgrade that improved the ergonomics and the software. The aspect ratio increased to 3:2, and each eye has a 2k display that lessens users experiencing eye fatigue. With an 8-megapixel camera, users can expect an improved visual experience as well.
4. Powerful Analytics for Knowledge
Since Microsoft created the Mixed Reality headset for enterprise, it has the analytics to keep up. So far, users of HoloLens 2 can:
Predict future data trends, thanks to the headset’s AI capabilities.
Place key performance indicators (KPIs) in areas that other users can see.
Share data via the cloud and across different headsets.
Virtually oversee and navigate inventory as the HoloLens 2 can collect information by looking at products.
5. Custom-built Infrastructure
HoloLens edges over other headsets with its custom-built infrastructure: the Azure Cloud. Microsoft created cloud services to help businesses face their challenges, enabling them to use their tools and frameworks to use and build applications across the network.
6. Comfortable for Long Wear
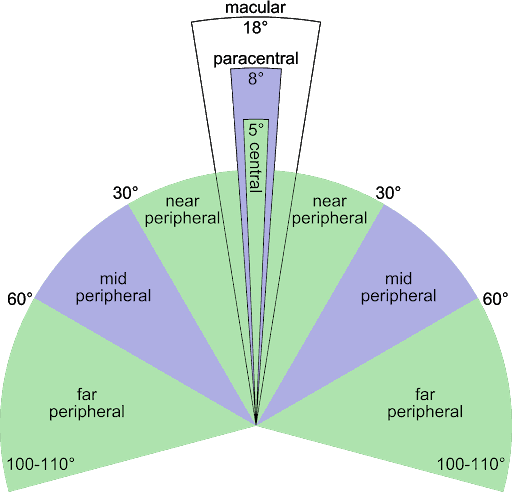
HoloLens 2 has a field view 52-degrees diagonal, an impressive upgrade from its predecessor’s 32-degrees diagonal. HoloLens 1 felt incomplete as the holograms would cut off the screen, even with slight head movements.
HoloLens 2 increased resolution - up to 2048 x 1080 per eye - offers a better immersive experience. Plus, the Mixed Reality headset’s features work seamlessly even when its user is wearing thick glass lenses.
Learning to Develop for the HoloLens 2
As mentioned earlier, Microsoft allows developers to contribute to HoloLens 2’s growth. The tech company even teaches newbie developers how to build their first augmented reality application for HoloLens 2.
During the course, developers will learn how to use the HoloLens 2 Emulator, for those who don’t own the headset. Learners must also install the most recent version of Visual Studio. They must follow a set of instructions before they can successfully deploy their apps on the HoloLens 2 app.
Magic Leap
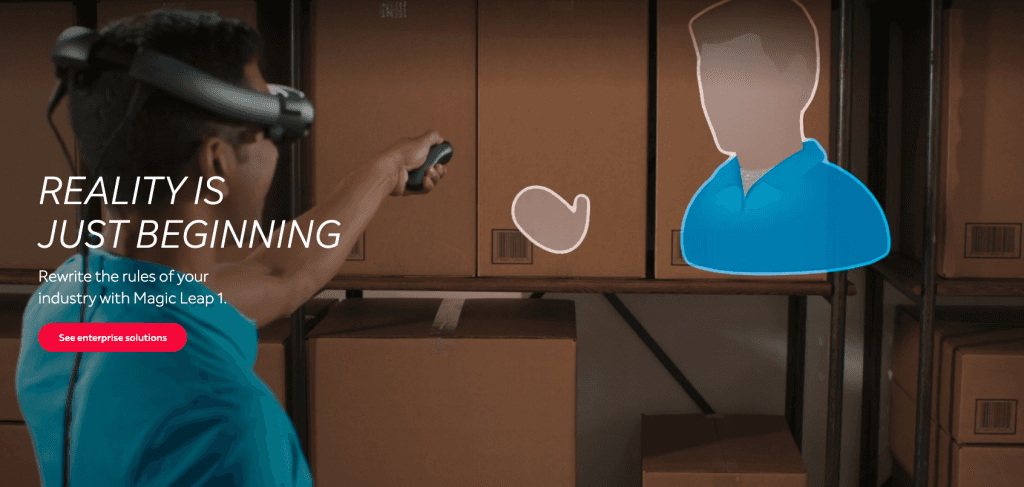
Launched in 2010, Magic Leap is a wearable computer that links the physical and virtual worlds. This Mixed Reality headset stands out with its lightweight, audio quality, comfort, and more. Let’s explore them in detail.
*There's one caveat when it comes to Magic Leap. Their promise and delivery were two different things. Make sure to do your own research before just looking at the stats.
1. Lighter Weight
Compared to other Mixed Reality headsets like HoloLens 2and Varjo XR-1, Magic Leap weighs less. It weighs 316g. Despite that, it has nine sensors that help it read and understand whatever space it's in - edges, corners, or surfaces.

2. Unmatched Volume of View
Users can seamlessly enjoy the view in front of them as Magic Leap allows them to see from 14.6 inches to the opposite end of a football field.

3. Topnotch Audio and Sound
Magic Leap boasts of Spatial audio that enables users to hear both virtual and real sounds simultaneously. This audio allows for a realistic attachment of sounds to digital objects.
Even if an evil dragon is walking stealthily behind you, you hear it before you see it. The Mixed Reality computer also allows the speech to text feature and has onboard speakers. Although HoloLens 2, Samsung MR, and Acer WMR also come with Spatial audio, HP MR and Varjo XR-1 do not.
4. Comfortable for Glass Wearers
Like Microsoft's HoloLens 2, Magic Leap caters to users who use glasses, mostly their shortsighted clientele. This Mixed Reality headset takes it even further by making prescription inserts available for its users.
The available inserts appear in the following ranges:
SPH: -7.5 to +3.0
CYL: -4 to 0
Total power (SPH + CYL): -7.5 to +3.0
Developing for Magic Leap
Magic Leap has a portal that allows developers to contribute to its growth. Although interested candidates need to have an account and log in before they can start work, Magic Leap provides several guides to help newbies get started or rusty developers to get their groove back.
To set up your Magic Leap for development follow this guide.
Acer Windows Mixed Reality Headset (WMR)
Acer's MR headset allows users to blend physical and virtual worlds to take their computing experience to a level where the senses get stimulated. Let’s explore how the Acer WMR Headset stands out.
1. Elite HMD Design
The design of the Acer WMR headset is unique. Asides from being more colorful with a blue front, users can lift the visor without taking off the entire headset. This is particularly useful for those that go in and out of VR to code or test.
Other headsets on the list don’t have the same flexibility. The HMD also has two motion controllers with a side grip button for gripping and picking up things.
2. Inside-Out Tracking
Thanks to its two front-facing cameras, the Acer WMR headset supports inside-out tracking. What does that mean?
Instead of having external cameras that track the HMD, the headset tracks itself. It achieves this by monitoring its movement relative to the external environment. This activity reduces a user’s need to calibrate multiple cameras and makes it easier to set the headset up in new spaces.
3. HoloReact Media Player
The Acer WMR headset comes with a HoloReact Media Player, which provides a 360-degree video and image experience. To use this, however, users should have:
An Acer WMR headset
A WiWR compatible PC running Windows 10 (Fall Creators Update),
Motion Controllers, or a mouse and keyboard,
An Internet connection to update drivers, etc.
Users should also ensure that their PCs match the Acer WMR headset’s requirements.
Developing for the Acer WMR Headset
To develop for Windows Mixed Reality, like the Acer WMR Headset, you’ll benefit from taking the XR Development with Unity course. This ten-week live online course will provide a foundation in growing one’s skills in building and prototyping MR, VR, and AR apps.
HP Mixed Reality Headset

The HP Mixed Reality headset provides users with a real escape into the virtual world while maintaining a grip in the real world. So how does the HP Mixed Reality headset stand out?
1. Effortless Set-Up
The HP Mixed Reality headset has a 2-in-1 cable that pairs HDMI 2.0 and USB 3.0 together, combines motion tracking and full software support. These features make it easy to plug and play instead of wasting time downloading additional software and setting up sensors.
2. Remarkable Comfort
This headset has an easy adjustment knob and front-hinged display for a superb experience. Even after hours of use, it remains convenient and comfortable.
3. Immersion Without Boundaries
The HP Mixed Reality headset has a program that’s dedicated to giving an unbeatable immersive experience. With up to 90Hz refresh rate and 1440 x 1440 resolution per eye, users will have crystal-clear visual quality. The headset is also equipped with six degrees of freedom (6DoF) with no tracking boundaries, allowing for liberating movement.
Samsung HMD Odyssey and HMD Odyssey+
Samsung offers users a taste of Mixed Reality with its HMD Odyssey series. The HMD Odyssey+ got launched in October 2018.
How the Samsung HMD Odyssey Mixed Reality Stands Out
The flagship HMD Odyssey has a dual 3.5” AMOLED display and offers a field view of 110 degrees. It has two 6DoF, an IPD sensor, a 3-axis compass, and a proximity sensor.
For sound, Samsung HMD Odyssey has an in-built AKG Spatial audio and two MIC support Cortana.
How the Samsung HMD Odyssey+ Mixed Reality Stands Out
The Samsung HMD Odyssey+ integrates an accommodating design with cutting-edge technology so users can have better immersive Mixed Reality experiences. Thus, it has a dual 3.5” Anti-SDE AMOLED display with up to 110-degree field of view. Plus, Samsung opted for a design with no external sensors, AKG headphones, and breathable fabric finish.
Varjo XR-1
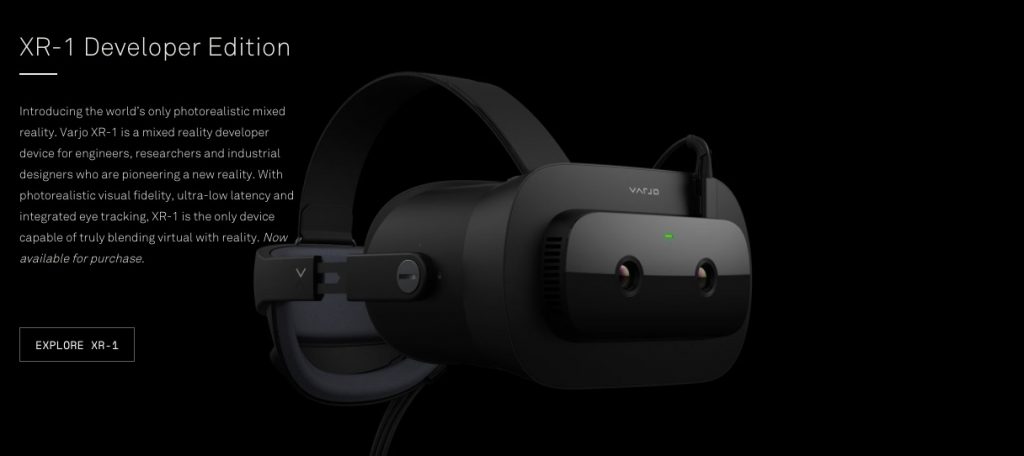

The Varjo XR-1 is a mixed reality device for engineers, designers, researchers who are pioneering a new reality. What makes the Varjo XR-1 unique? Let’s find out.
Photorealistic Mixed Reality
This feature would allow users to remove, add, and adjust colors, lights, and shadows. Users can replace real objects with virtual ones and even simplify or blur the objects, and no one will be the wiser.
The Varjo XR-1 will also come with a cockpit-based XR solution that enables the pilot and co-pilot to connect with the physical cockpit while in a synthetic environment. This feature will allow never-before-seen immersion and interactions in Mixed Reality.
Generate True-To-Life Interactions
Varjo’s XR-1 Developer less than 20milliseconds latency image pipeline will let users explore true-to-life virtual worlds as natural extensions of the real world.
The Mixed Reality headset’s low latency will allow professionals to explore mixed realities the same way they’d experience the real world. With this feature, one can discuss, create, collaborate, or even drive a car in Mixed Reality.
Impressive Eye Tracking
Users can enjoy sub-degree accuracy integrated 100 Hz stereo eye-tracking. This feature will deliver precision across real and digital environments, even when wearing contact lenses or glasses.
Developing for the Varjo XR-1
Varjo XR-1 offers developers native SDK and plugins for Unity and Unreal Engine. If a developer has an existing project built with Unreal or Unity, it’s easy to port it to run on XR-1 Developer Edition.
To start developing for the any mixed Reality headset, you’ll want to take the XR Development with Unity course. The ten-week online course will prepare them to be a Unity Associate certified in Artist, Programmer, or Developer.
What’s the Best Mixed Reality Headset?
Each MR headset has unique strengths and weaknesses. It’s up to you to choose what fills your needs best. Instead of settling for an arbitrary best-headset, We've highlighted their strengths and weaknesses. That way you can choose what’s best for you.

12 Real-World Applications of Mixed Reality
Although Mixed Reality is in its infancy, it's already gaining usage across different fields and industries. Here are some real-life applications of this technology.
1. Manufacturing
Not many technologies can boast of the benefits that Mixed Reality offers manufacturing. The technology takes the data captured by the internet of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) systems and makes them instantly useful to engineers and manufacturing teams. Workers can visualize and use the data in real-time while they’re on the job.
With MR, an inspection worker could visually retrieve information about energy consumption and see how individual components of a device are working as he walks through a plant. Plus, Mixed Reality permits both maintenance and inspection staff to confer with a remote expert if they run into a strange problem.
Teams in manufacturing can also create virtual instructions and cues that others can follow. For example, if a manager highlights a particular location or device, his workers know that it requires their attention.
Mixed reality also supports devices, like helmets, headsets, and glasses that are IoT-enabled, so they can interact with other devices, retrieve data through their sensors, and distribute the data collected through a network. These devices empower workers to make better predictions and timely decisions.
2. Space Science
In October 2018, OnSight won NASA’s Software of the Year Award because it helped engineers and scientists to explore Mars virtually. This mixed reality software is a collaboration between NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Microsoft. In addition to studying Mars’ geology, InSight also permitted remotely located scientists to walk around, meet, and communicate with one another in real-time.

3. Automotive
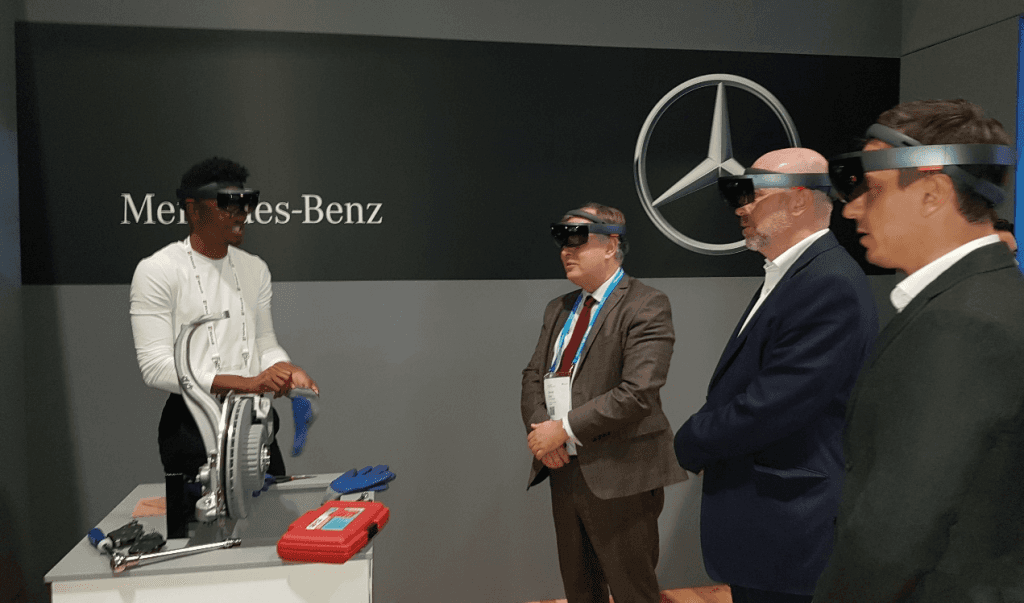

Image credit: Windows Experience Blog
The automotive industry is also reaping the benefits of Mixed Reality. In 2018, the Mercedes-Benz Global Training illustrated how HoloLens could improve engine manufacturing and brake assembly efficiency.
4. Aviation
Aviation solutions using Mixed Reality can provide real-time experiential training and drive up digital manufacturing strategy. Airbus tested this theory with its Microsoft collaboration in June 2019. The aircraft manufacturer tested how Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 headset would work in a Mixed Reality environment. The test areas included training, design, and manufacturing.
Another example is BAE Systems, which manufactures the electric propulsion Systems for HybriDrive buses. BAE worked with PTC, a Microsoft Mixed Reality Partner, to create Mixed Reality solutions that enhance Firstline Workers’ efficiency.
BAE and PTC used ThingWorx Studio to create a detailed step-by-step training guide for Microsoft HoloLens. The guide instructed workers on how to assemble a green energy bus battery.
5. Holograms
Thanks to MR, people can generate holograms to show scenes or objects that never existed. In January 2016, Mixed Reality company, 8i, premiered a realistic hologram of John Hamm for that year’s Sundance Film Festival.
The company also created a Buzz Aldrin holographic image for South by Southwest (SXSW). 8i even built an app that allows users to generate their 3D animations.
Even celebrities are getting in on this action. Kanye West gave his wife, Kim Kardashian West, a hologram of her late father for her 40th birthday.
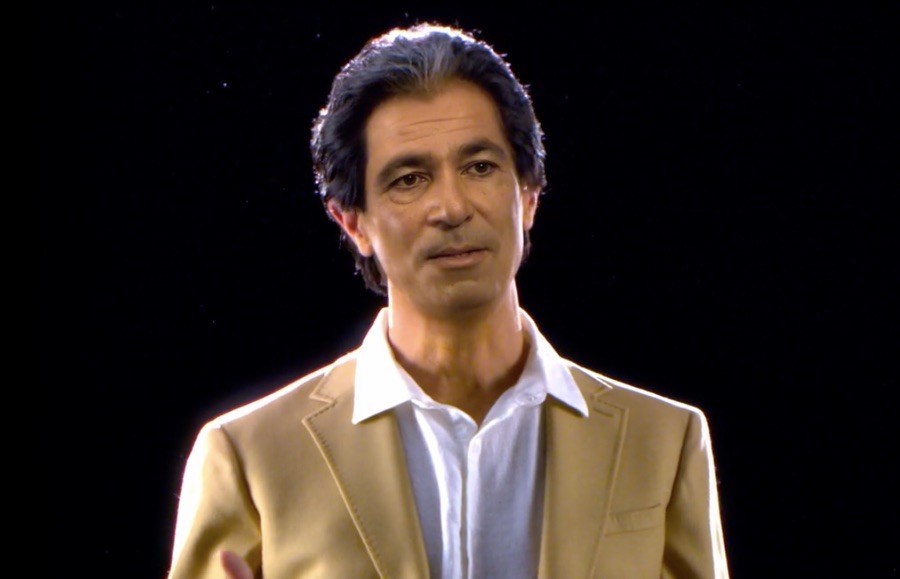

Kaleida created the Robert Kardashian hologram. Kim was so delighted that she shared the clip on Twitter.
6. Education
Some MR apps can help students learn through communication with virtual objects. Others, like HoloAnatomy, allow teachers to instruct students remotely.

Image credit: Case Western Reserve University
Developed by Cleveland Clinic and Case Western Reserve University, the app uses Microsoft’s HoloLens to teach medical students anatomy. It even won the Virtual Reality & Augmented Reality award in the 2016 Jackson Hole Science Media Awards.

GIGXR is also making waves with its immersive learning mixed reality platform for healthcare. Their best apps, HoloPatient and HoloHuman, use lifelike 3D simulations in a coordinated physical space.
7. Sports and Entertainment
Sports and entertainment fans get something from Mixed Reality too. Years back, PGA Tour developed an app that gave fans a 3D experience of golf courses.
Even the Golden 1 Center showed that fans could enjoy a basketball game differently. The home of the Sacramento Kings offered fans a chance to find live data interactions.
These interactions include facts on players, digital agendas, and ordering merchandise and refreshments to their seats.
8. Healthcare and Medicine
With Mixed Reality, medical professionals can view and share patient records or data in a more interactive form. They can also enjoy better imaging.
Rather than using a keyboard and mouse to zoom in on parts of a scan, they can use Mixed Reality to track where a user is looking and even respond to gestures. This way, medical professionals have a more realistic way of analyzing an image.
Since Mixed Reality devices can record and share voice communication, healthcare professionals can send and receive voice communications quicker.
9. Remote Work
Remote workers can communicate with co-workers or clients through Mixed Reality. Users can even bypass language barriers by using translation applications that translate different languages in real-time. Japan Airlines uses HoloLens to train engineers without being physically present in the hangar.
10. Railway Maintenance
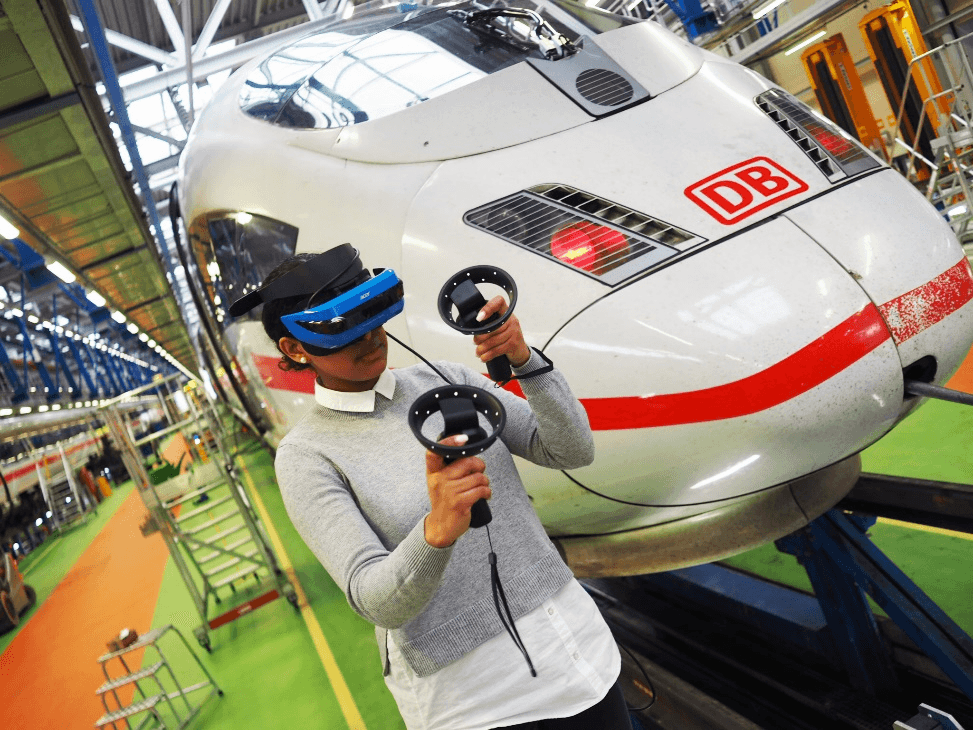

Image credit: Windows Experience Blog
Since railroad facilities and installations are continually evolving, engineers and maintenance teams need to learn how to use new technologies quickly. That need prompted Deutsche Bahn’s involvement in the Microsoft Mixed Reality Partner Program.
The German railway company subsequently built an app that would train engineers on railway maintenance and parts more efficiently.
11. Construction and Engineering
Instead of working physically, inspectors and engineers can view their sites through a visual headpiece, allowing them to identify problems or collaborate with on-site workers in real-time. Like Trimble Connect for HoloLens, an app can link 3D content from the screen to the construction site.
The app provides 3D design review, coordination, collaboration, and project management processes.
Put Mixed Reality to Work
The applications available for MR tech are unbelievable, but it’s just the beginning as the technology is still growing. Only time will tell where MR will take us, but we can benefit from the experience it’s bringing us until then. Put mixed reality to work for you.


