Table of Contents
#
360 Video
A 360-degree video is a type of immersive video content that is simultaneously captured in all directions. Such an immersive surround format allows viewers of 360 videos to freely look around during the playback while their point of view stays fixed unlike with traditional 2D videos where both points of view and the viewing angle are out of viewers’ control.
In most cases, 360 videos are recorded using a rig of cameras or an omnidirectional camera with multiple lenses that can film overlapping angles simultaneously. 360 videos can also be recorded in virtual reality simulations using either development tools such as Unity or 360-recording apps while using a virtual reality headset.
360 videos can be viewed either using video players that support interactive “magic window” 360 formats (e.g. Youtube 360) or using virtual reality headsets.
3D Model
A 3D model is a virtual representation of an object or a surface that is created using 3D modeling software. A 3D model consists of polygons that are essentially points or dots connected in 3D space. Connected with each other, polygons define edges and planes that serve as structure of any 3D model. The higher the polygon count, the more complex the final 3D model can be. Through added textures, dynamic lighting, and materials 3D professionals can create highly-realistic 3D models of either real or imaginary objects.
(Source)
3D models are widely used in architecture, engineering, marketing, animation, gaming, movies, augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality simulations.
3DOF
3DOF, or three degrees of freedom, refers to the number of ways an object can move through space. 3DOF includes rotational movement along three-axis: x, y, and z, otherwise known as pitch, yaw, and roll. Most commonly 3DOF is used as a term in virtual reality to describe a number of user movements that a virtual reality headset can detect. A 3DOF virtual reality headset can detect when a user looks up and down, left and right, or when they tilt their head to the left or right. That means the 3DOF headset will not register when you sit or move forward, or step to the side.
Early VR headsets supported only three degrees of freedom as a way to cut production costs, but every modern VR headset surpassed these limitations and now supports all six degrees of freedom (6DOF).
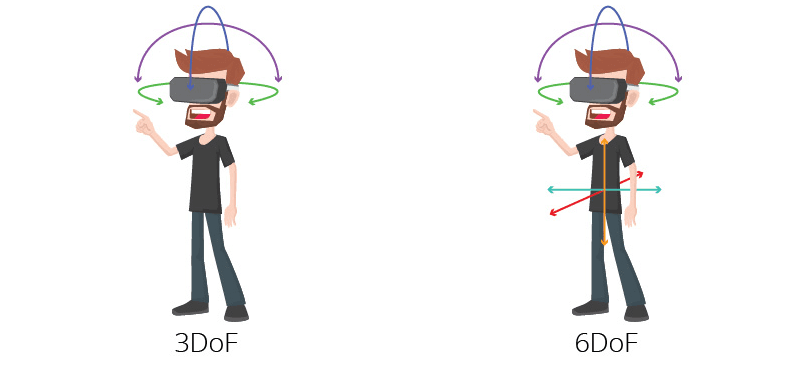
(Source)
Examples of virtual reality headsets that support only three degrees of freedom include Oculus Go, Daydream VR, and Google Cardboard.
6DOF - Six Degrees of Freedom
Six degrees of freedom, or 6DOF, describes the number of possible ways an object can be moved through space. The term is typically used in virtual reality to describe how many user movements a virtual reality headset and controller can detect. 6DOF includes three rotational movements (x,y,z, or pitch, yaw, and roll) and three translational movements along the same axis (moving forward and backward, moving left and right, moving up and down).
All modern VR headsets support six degrees of freedom which is the maximum possible level for any rigid body moving in space.
Examples of VV headsets that support 6DOF include Oculus Quest 2, Valve Index, HTC Vive Pro, Pimax 8KX.
A
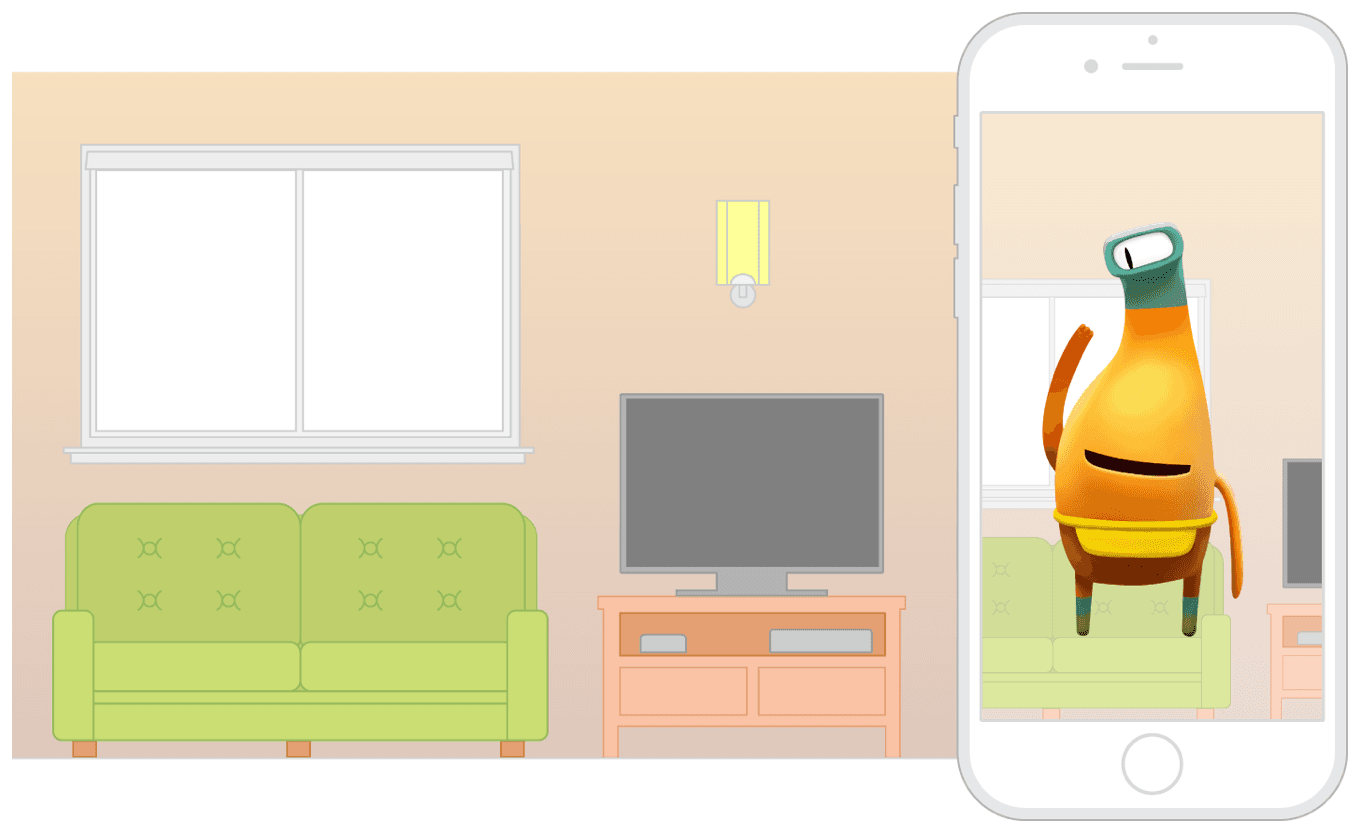
AR - Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) refers to the way of interacting in real-time with digitally generated objects and contents that are embedded into the user’s real-world surroundings.
Unlike virtual reality, augmented reality doesn’t replace a user’s surroundings completely with a virtual simulation. Augmented reality can either incorporate virtual objects into a real-world environment (constructive simulation) or mask and replace some real-world elements with virtually generated (destructive simulation).

(Source)
Augmented reality is experienced through an AR device such as AR glasses or AR headset that precisely scans and maps out a user’s real-world environment in order to accurately integrate digital content into the scene. AR simulations are used in mixed reality business simulations, training, marketing, and entertainment.
ARCore
ARCore is a platform for building augmented reality applications that work with Android phones and iOS devices (iPhone, iPad). ARCore was released by Google in 2018. The platform uses built-in mobile device cameras to track the position and orientation of a device, understand the real-world environment and properly embed digital content within the scene.
ARCore can also estimate average lighting in the scene and detect flat surfaces. ARCore can also be used for object recognition apps, virtual object placement, gaming applications, or any other app that can benefit from embedding digital content into the real world scene through the use of the mobile device.
ARKit
ARKit is a software development kit (SDK) for developing augmented reality solutions for iOS devices. ARKit was released by Apple in 2017 and currently supports only applications for iPhone 6s and iPad Pro or later.
(Source)
The latest ARKit 5 version features location anchors for creating city-specific AR experiences, improvements to motion tracking, expanded face tracking support, and plane detection using a built-in LiDAR scanner in the newest iOS devices.
The platform was built on top of a SceneKit framework and completely replaced its functionality.
B
Blender
Blender is an open-source 3D graphics software that can be used for creating 3D models and scenes, rigging, animation, texturing, and rendering. Blender can be used for creating 3D animated scenes, visual effects, and 3D models. The software is actively used in gaming, animations, 3D printing, AR, and VR industries.
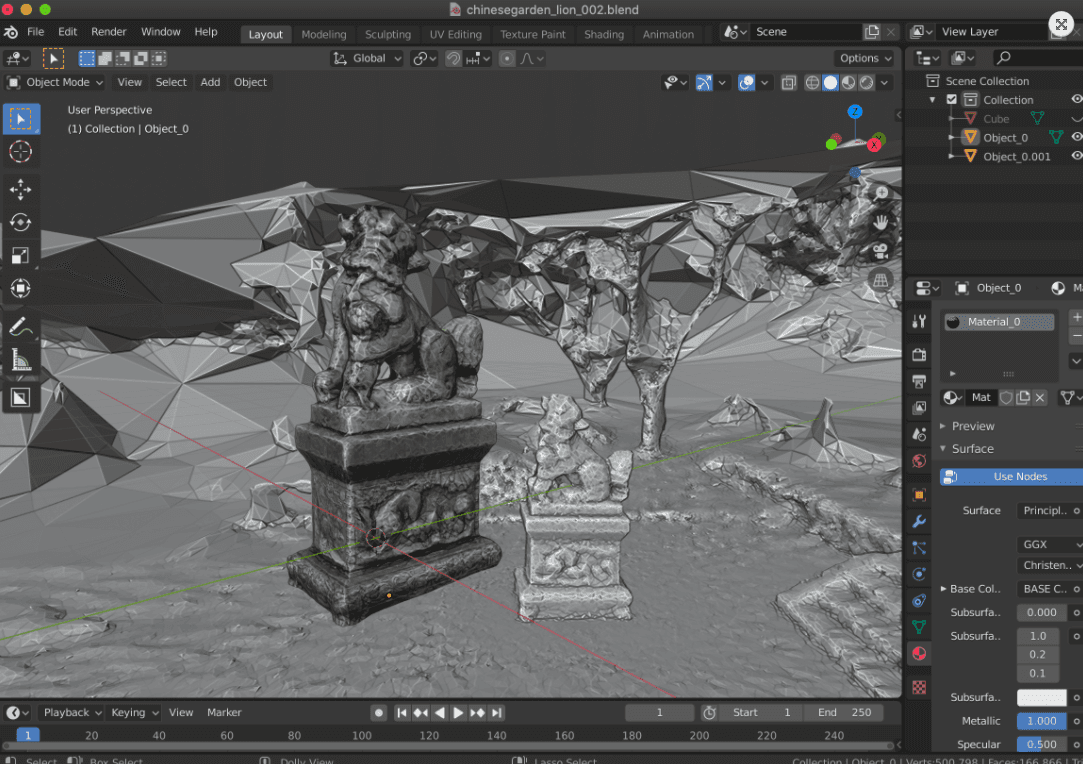
(Source)
Blender is written using Python programming language and supports Python scripting for creating custom workflow tools or automation. Blender is free software released under General Public License that can be used for creating commercial 3D projects without additional licensing costs.
C
CAD
CAD, or computer-aided design, is a process of creating design solutions with the support of a computer environment. Computers allow designers to optimize parts of their workflow, speed up calculations and simulations, increase the quality of design, enhance communication and collaboration, and create a digital database for storing and reusing valuable assets.
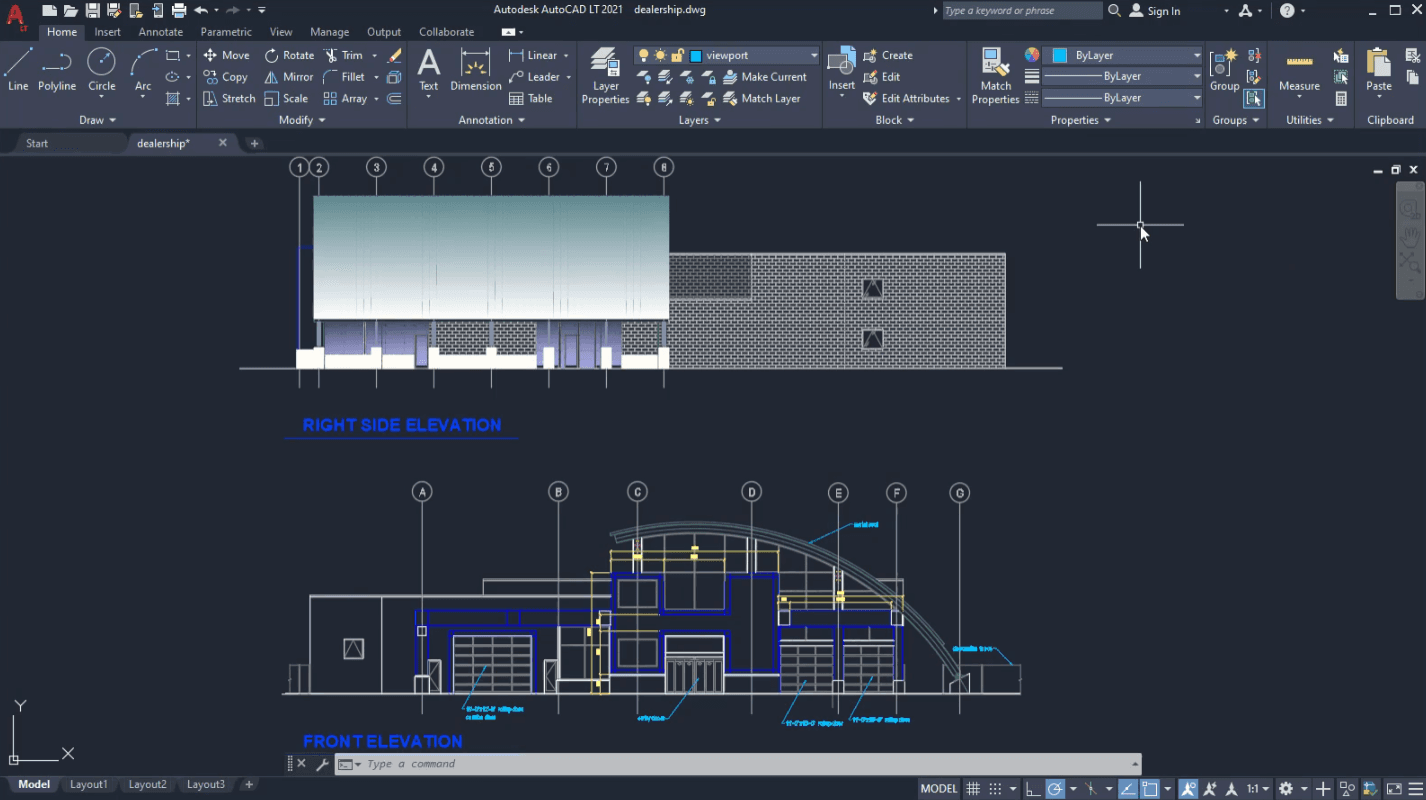
(Source)
Examples of CAD include civil engineers using AutoCAD for creating piping systems, user experience designers using Figma to create a prototype of a web service, or virtual reality developers using Unity3D to create ultra-realistic simulations (“digital twins”) of a business workflow.
CPU (Computer Processing Unit)
CPU, a central processing unit, is a hardware component of a computer and a control center that runs stored program instructions. CPUs consist of three parts: a control unit that acts as a control center, a logic operation unit for executing all arithmetic and logical operations, and a storage unit (i.e. processor register) that provides space for storing data and instructions.

(Source)
The CPU interacts with the computer’s primary memory storage and relies on it for both data and instructions. CPU is complex electronic circuitry made up of transistors that regulate the operation. CPU performance increases with the number of transistors.
D
Digital Twin
A digital twin is a virtual asset that is designed to accurately replicate a real physical object in a virtual 3D space. Digital twins are often used in virtual training and testing complex simulations as a virtual environment allows for quick iteration, low-cost scaling, advanced real-time feedback, and accurate automatic data collection.
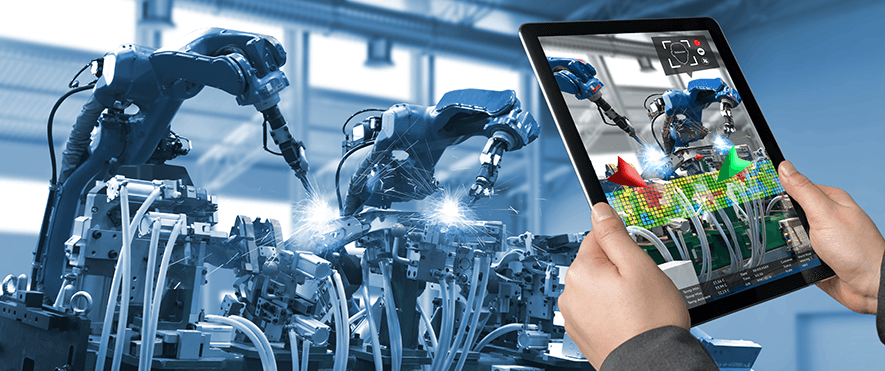
(Source)
Examples of digital twins include creating a virtual representation of a manufacturing process for training new engineers, creating a digital car prototype for crash simulations, or creating a replica of a house or a museum for demo purposes.
E
Eye Tracking
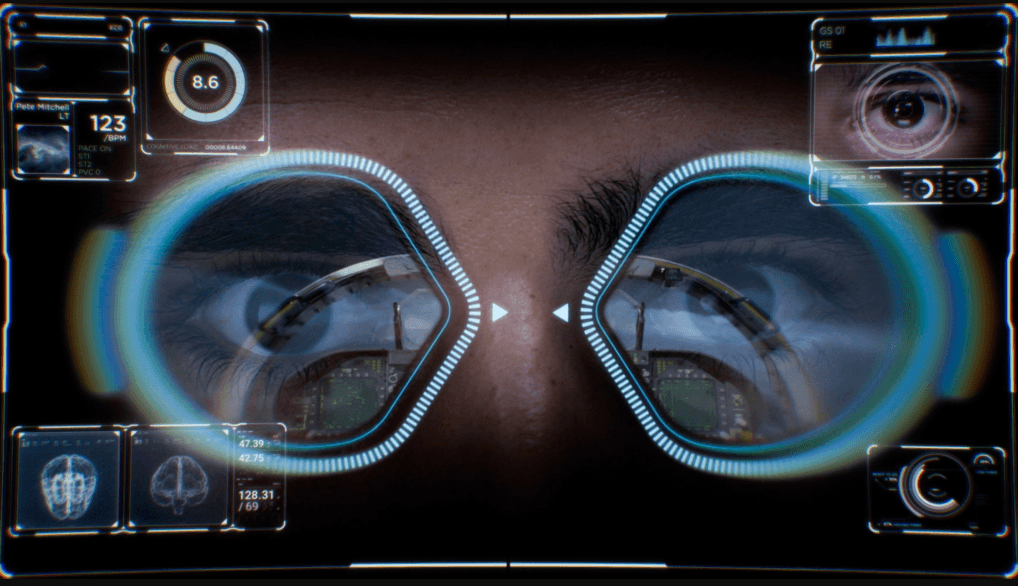
Eye-tracking is a sensor technology used for detecting a person’s eye movements. Eye-tracking helps understand where an individual is looking, what they are focused on, and how long they gaze at a particular point. Eye-trackers detect eye movements using high-definition cameras that record a reflection of near-infrared light off of the cornea.

(Source)
(Eye-tracking technology is commonly used to better understand individual behavior in scientific research, business applications, and entertainment. There are standalone eye-tracking devices and devices with integrated eye-tracking such as virtual reality headsets or augmented reality glasses. Examples of VR headsets with built-in eye-tracking include HP Reverb G2 Omnicept, Varjo VR-3 and XR-3, and Xtal 8K.
F
Face Tracking
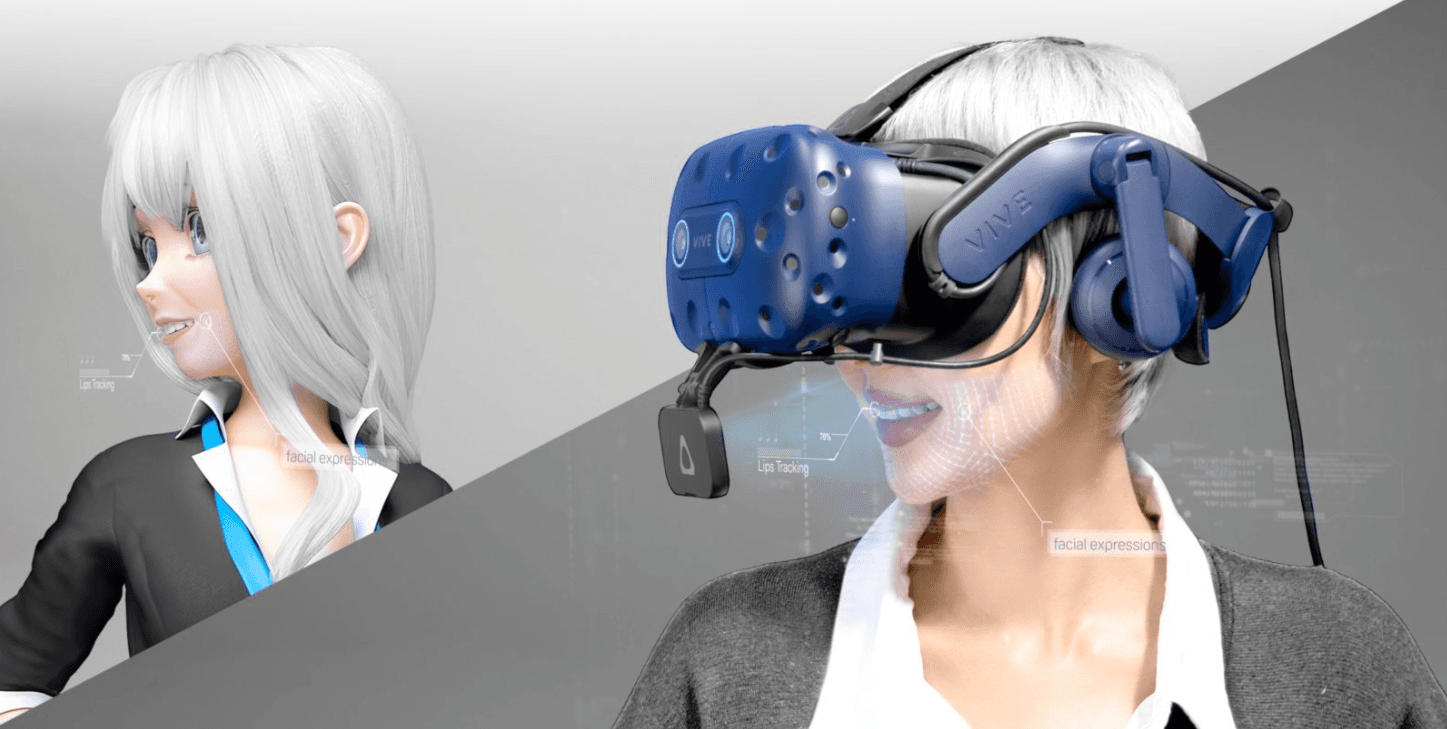
Face tracking is a sensor technology that detects human faces and tracks facial expressions, head position, and gaze in real-time. Face tracking is typically implemented using one or several cameras and software trained to recognize a range of facial movements from a live stream video feed.

(Source)
Face tracking allows for recognizing human emotions, creating highly-immersive digital avatars, or registering human behavior in real-time. Face tracking technology can be used for enriching virtual reality interactions, conducting medical and scientific research, or remote collaboration and education. Notable devices with face-tracking technology include Vive Facial Tracker and HP Reverb G2 Omnicept headset.
FOV - Field-of-View
The field of view (FoV) indicates how much of the world can be observed at a given moment through human eyes. The horizontal field of view of an average person is between 170 and 175 degrees. In virtual reality, an FoV similarly refers to how much of a virtual world can be seen at a time.
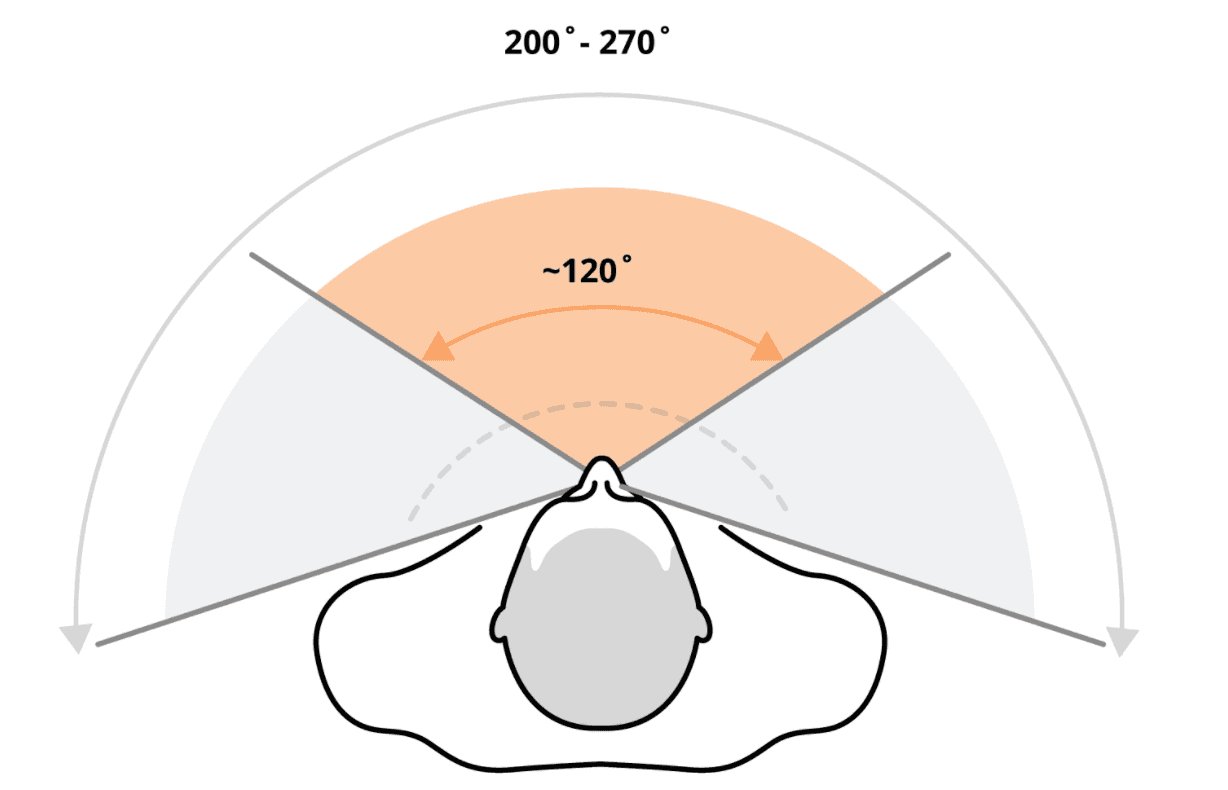
(Source)
FoV in virtual reality is defined by VR headset lenses and display configuration. The higher the field of view of a virtual reality headset, the more immersive and convincing a VR simulation can be to a human’s eye. Early headsets such as Oculus Go sported FoV of about 100° whereas modern high-end headsets such as XTal 8K provide FoV of 180 degrees.
Foveated Rendering
Foveated rendering is a technology that facilitates highest image quality rendering in the user's focus view area while reducing image quality in the peripheral view. There are fixed and non-fixed foveated rendering approaches: the former assumes a fixed user focus area at the centre whereas the latter works with eye tracking technology to detect where the user's eyes gaze is currently focused.
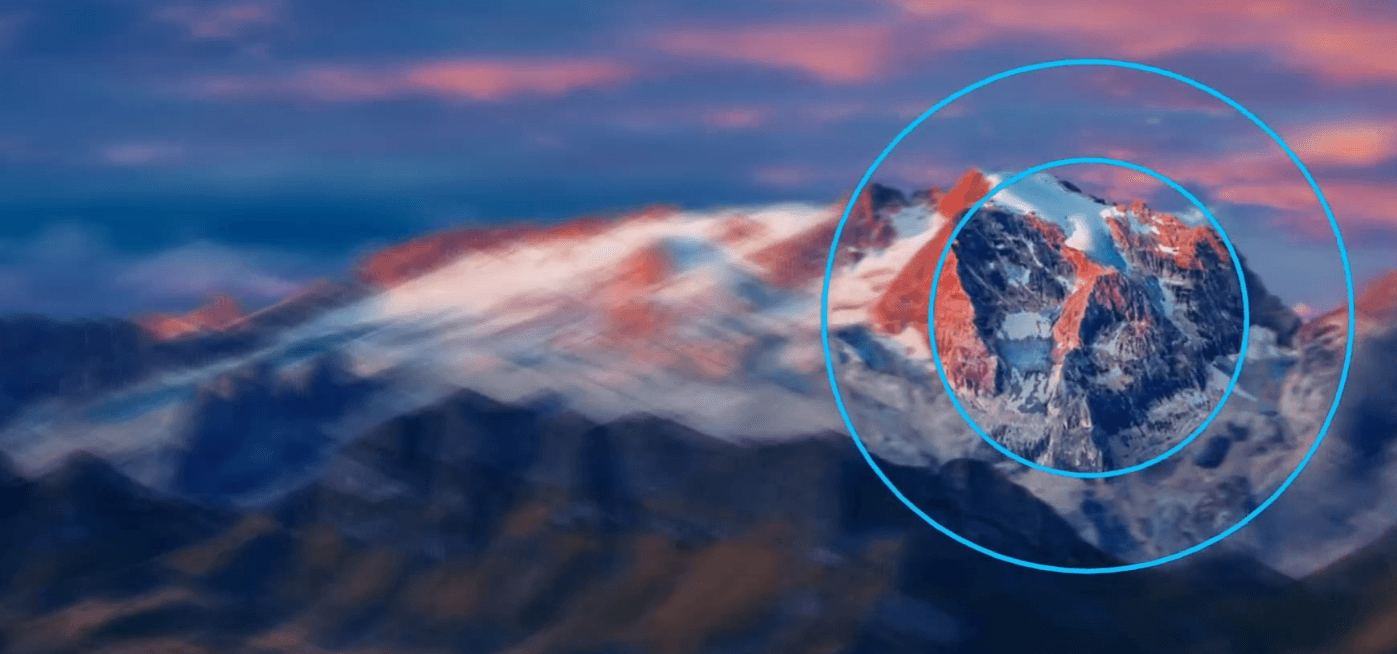

(Source)
Foveated rendering is used in virtual reality to reduce computational load on the headset or PC and achieve a realistic viewing experience by mimicking how human vision works.
Frames-Per-Second (FPS)
Frames-per-second (FPS) is a visual output parameter that describes how quickly a sequence of images replace each other. In virtual reality, the greater the FPS, the more immersive and smooth the user’s visual experience. Higher FPS often comes at the cost of higher required computation power.

(Source)
An optimal FPS for pleasant VR experience is at 90 frames per second, however modern high-end VR systems are capable of providing a higher FPS. Low FPS in a virtual reality simulation can lead to disorientation and motion sickness as a result of inconsistency between user’s actions and visual feedback from an environment.
G
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
Graphics processing unit (GPU) is a computer processing element in the form of an electronic circuit that is used for processing various aspects of visual and nonvisual applications. Due to parallel structure GPUs are more effective than central processing units for processing large blocks of data.

(Source)
For visual tasks, GPUs are used in rendering, shading, lighting, and visual effects. For non-visual tasks, GPUs are used in machine learning, blockchain calculations, artificial intelligence, and high-performance computing.
Hand Tracking
Hand tracking is the technology for detecting precise hand movements and finger movements in real-time. Hand tracking is used in virtual reality to accurately detect, register, and render user movements in a virtual simulation.
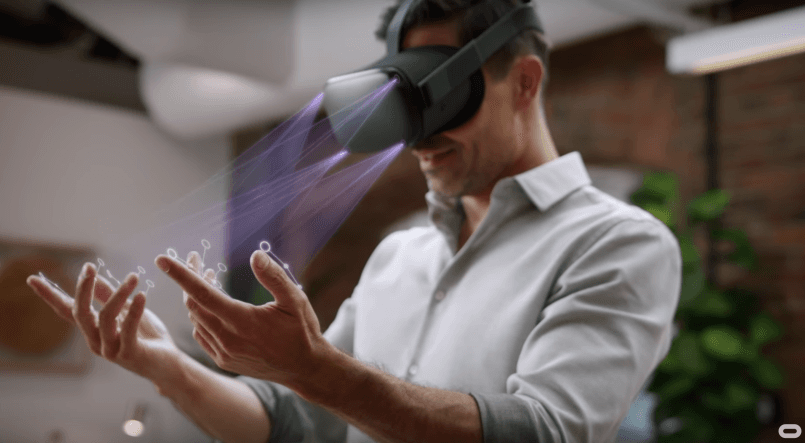

(Source)
Hand tracking is typically implemented using inside-out tracking through built-in headset cameras and software that is trained to detect hand and finger positions from any angle of view. Alternatively, there are outside tracking systems that utilize external tracking stations and various sensors located on either user’s hands or hand controllers.
Haptics
Haptics in virtual reality refers to the technology of conveying and transmitting tactile sensations in virtual reality environments. As a broader concept, haptics applies to anything involving touch. Haptic interfaces improve VR immersion by letting users interact with virtual reality objects through haptic feedback, a physical tactile sensation that hints at the interaction between the user and a virtual object.
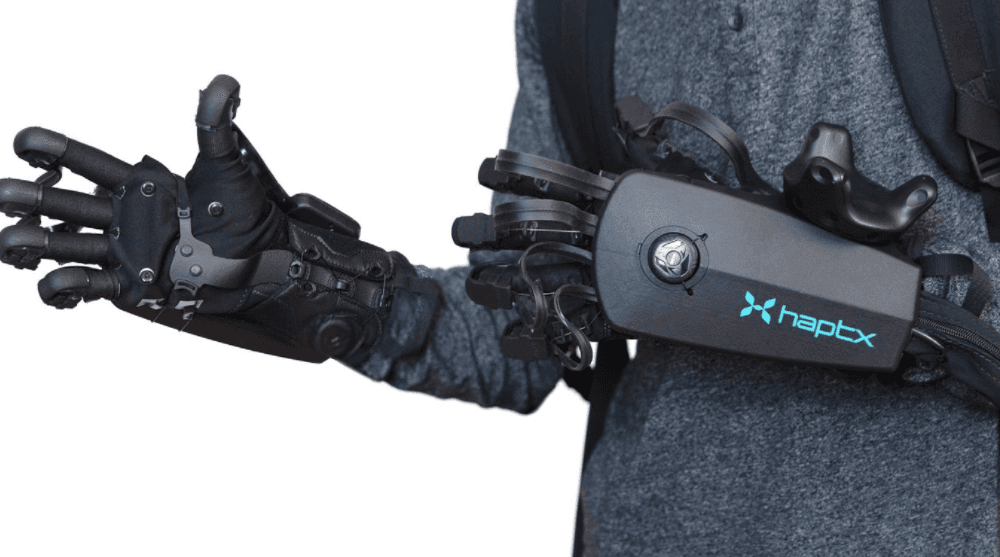

(Source)
The most common examples of haptic feedback are mechanical vibrations in VR and gaming controllers. More advanced examples of haptics include microfluidics, friction modulation, ultrasound, and lasers.
HMD (Head Mounted Display) or Headset
Head Mounted Display (HMD) is an electronic device that sits on a person’s head and provides visual imagery through a display located at the person’s eye level. An HMD typically has either one display for both eyes or two displays for each eye.
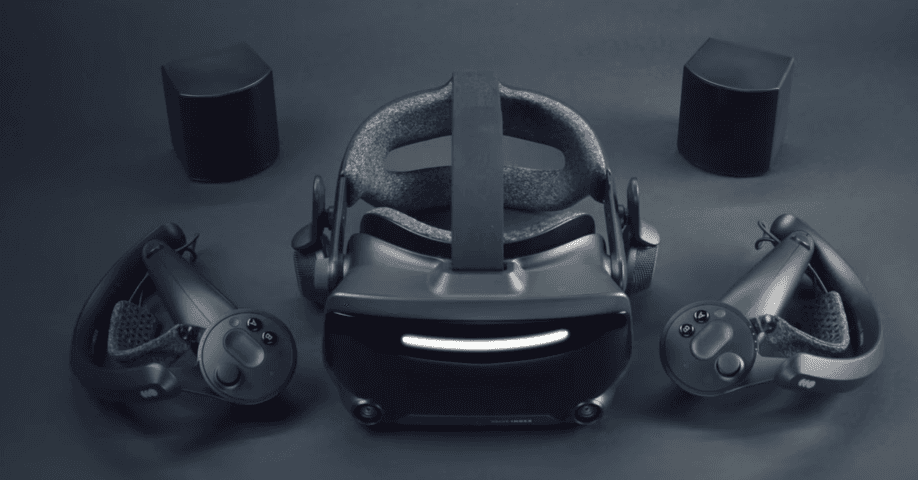

(Source)
One of the most common examples of an HMD is a virtual reality headset that is essentially an HMD combined with a spatial audio system, positional and movement tracking system, and comfort adjustments.
I
Immersion
In virtual reality, immersion refers to the state of being physically immersed in a virtual world. The immersion state is created using a visual virtual environment, haptic feedback, spatial audio, and other stimuli to further immerse the user into a virtual world.
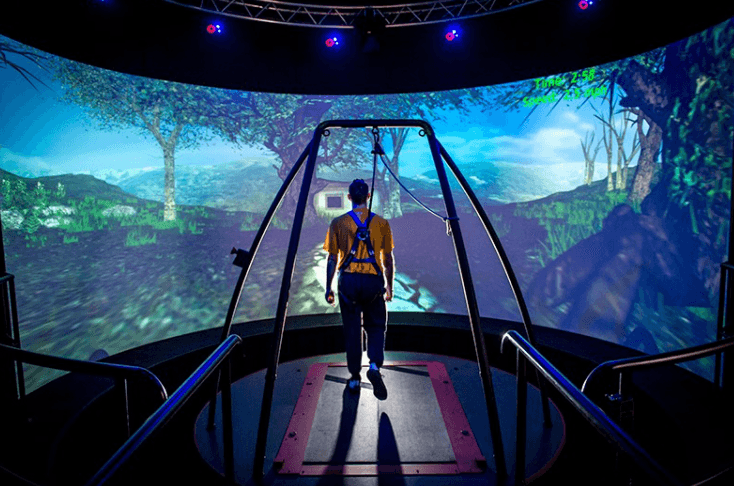

(Source)
Lifelike virtual world imagery is not as crucial for achieving VR immersion as low-latency and accurate motion tracking. Modern virtual reality systems strive to elevate the immersive state through precise hand tracking, high-definition imagery, maximum long-term comfort of wearing a device, and a tetherless experience.
IPD - Interpupillary Distance
Interpupillary distance (IPD) is the distance between the centers of a person’s eyes. The IPD of every person is slightly different and typically sits in the range between 54 and 72 millimeters with the majority of people having an IPD of around 61-65 mm.
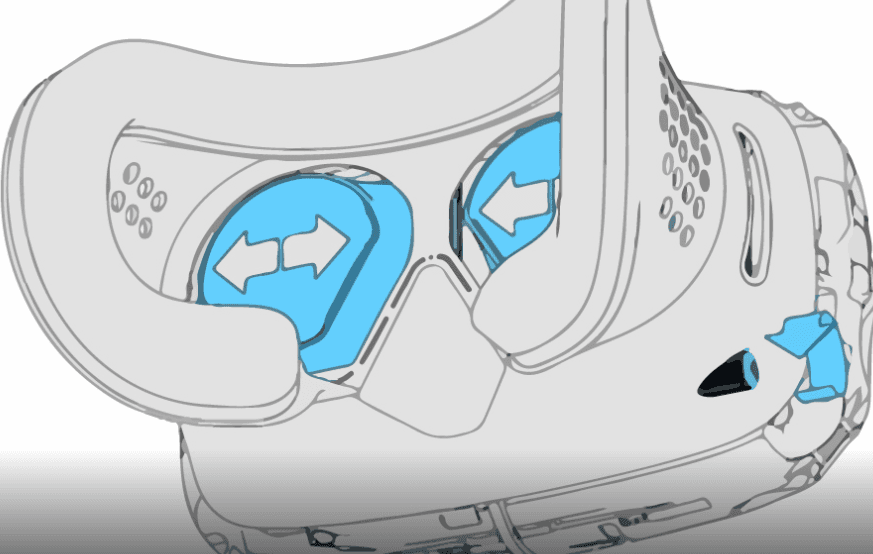
(Source)
For virtual reality headsets, IPD is a crucial characteristic as the distance between headset’s lenses should correlate with a person’s individual IPD. If there’s a mismatch between the lenses distance and a person’s IPD, a user will experience dizziness and blurriness. Most VR headsets provide either manual or automatic IPD adjustment so that every user could set up their headset optics for optimal comfort.
L
Latency
Latency is a time delay between an agent’s action and response. Latency is typically measured in seconds and milliseconds and reflects how quickly a user’s environment reacts to their actions.
In virtual reality, low latency is a prerequisite to a smooth and immersive virtual experience as any delay in registering user’s actions, interface feedback, or virtual environment response would diminish user experience and a sense of legitimacy of a virtual world. In augmented reality, a high latency leads to misalignment between real-world and digitally embedded content.
LiDAR
LiDAR, or light detection and ranging, is a remote sensing method used for measuring the exact distance of an object on the earth’s surface. Even though it's a fairly old technology (it was used in 1960s for the first time) it is seeing resurgence today in AR applications.
Apple included LiDAR tech to the iPhone 12 Pro (Max), iPhone 12 Pro Max, or 2020 iPad Pro. LiDAR enhanced Apple's AR capabilities, particularly when it comes to scanning real-world environments and displaying virtual objects within them.
Locomotion
Locomotion is an object’s ability to move in a physical space. In virtual reality, locomotion refers to a user’s ability to freely move through a virtual space without being restrained by real-world location limits such as a small room or a fixed position.
Ensuring proper locomotion lets users fully experience the virtual world. Locomotion in VR is one of the pillars of digital immersion that facilitates advancement in virtual reality controls (VR controllers) and supporting devices (VR treadmills, neural feedback devices).
M
Metaverse
Metaverse is an encompassing experience of living in a virtual world. Metaverse combines advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, blockchain technology, the internet, and others to enable people to work, entertain, collaborate, and communicate with each other within the digital universe.

(Source)
Although there’s no straight definition of the metaverse form yet, a metaverse supposedly brings a multitude of 3D worlds together and blends over both economical and sociological aspects of both the digital and physical environment of people.
MOCAP - Motion Capture
Motion capture, or MOCAP, is a technology that captures objects’ of people’s movements and expressions for the purposes of digitalization and research. MOCAP technology uses several cameras to capture movements in low-latency and map the animated data to a 3D model the serves as a digital actor.
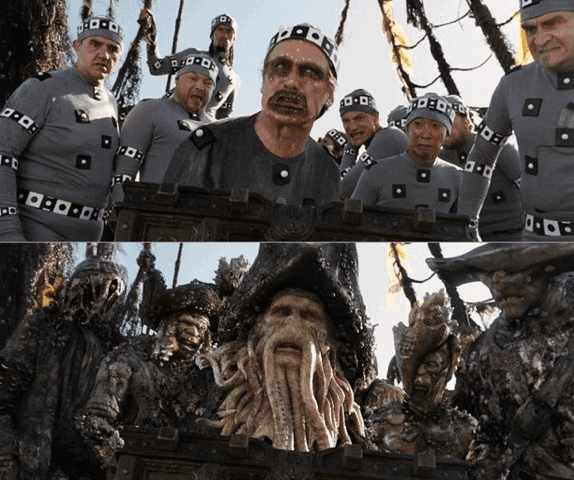

Motion capture is used in movies, game development, virtual reality applications, research, and augmented reality to ensure realistic animation and improve the cost-efficiency of production.
MR - Mixed Reality
Mixed reality is a combination of the real and digital world to elevate the technological capabilities of both. Common benefits of mixed reality include the ability to generate highly accurate simulated training and experimental environments, bring digital computing capabilities further into the real-world environment, or achieve higher personal productivity. Mixed reality solutions utilize both augmented and virtual reality technologies to achieve the desired outcome.
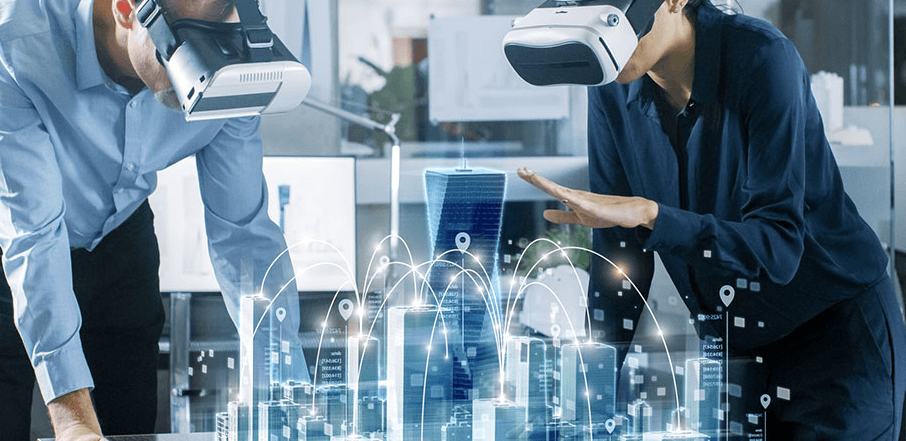

(Source)
Examples of mixed reality applications and projects are virtual business training simulations that reduce training costs and improve product safety, virtual remote collaboration, and educational presentations.
O
Occlusion
Occlusion is an event that happens when one object blocks another one in a 3D space. In virtual reality, occlusion is commonly used to describe a positional tracking issue, for example, when a built-in camera tracking system can’t detect the position of one virtual controller because it’s blocked by another one.

(Source)
Most optical tracking systems are subject to occlusion events and thus employ additional methods to ensure proper tracking, including predictive algorithms and assisting tracking systems.
OpenXR
OpenXR is a royalty-free and open standard API to help AR and VR developers build applications that operate across a wide range of devices. OpenXR was released by Khronos Group in 2019. The standard aims to bring together a disjointed field of VR and AR development devices and tools that either require too much additional development to ensure cross-platform functioning or don’t work together at all.
OpenXR currently supports Microsoft HoloLens 2, Oculus PC platform, Valve SteamVR, Varjo, Unity, Unreal Engine, and others.
P
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the process of obtaining trustworthy information about the environment and physical entities within it through the acquisition and evaluation of photographic imagery.

(Source)
Photogrammetry is used in virtual reality to help generate a digital representation of real-world locations, create accurate location-based virtual simulations, or study physical locations and objects in a digital virtual environment.
Polygon
Polygon is a geometrical element used in 3D modeling as a building block for composing and rendering a digital model in a three-dimensional space. Polygons are typically formed by connecting at least three points or vertices in a 3D space.
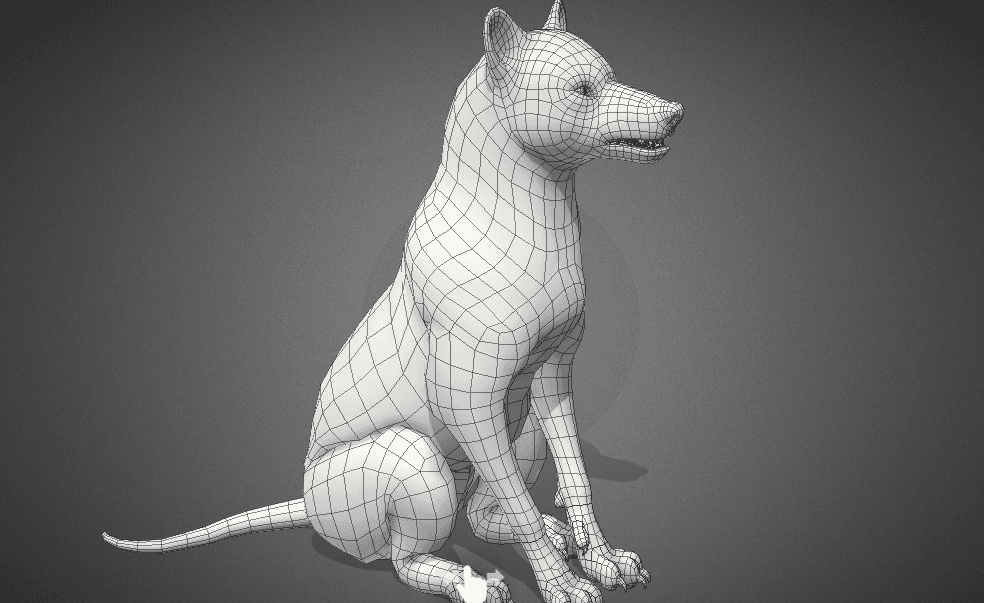
(Source)
A group of polygons forms a polygon mesh that represents the shape of an object in space. The number of polygons in 3D models defines how detailed the 3D model will be and how much computational resources it will require to be animated and rendered. There are high-poly and low-poly 3D models.
Prototyping
Prototyping is a process of creating a tangible representation of an idea for testing or validation purposes. Prototypes can take any form and complexity from rough paper sketches to detailed 3D models and experimental physical models. The main purpose of prototyping is to validate ideas before mass production, receive critical feedback, or kickstart an iterative creative process.
(Source)
The main advantages of a prototyping process are flexibility to make necessary changes on the go, lower cost compared to high-end production, and a sense of progress.
R
Rendering
Rendering is the process of generating an image, a video, or a real-time stream from a two or three-dimensional object or a scene using a rendering engine. Rendering is typically the final step on the digital graphic pipeline to produce the final visual output.
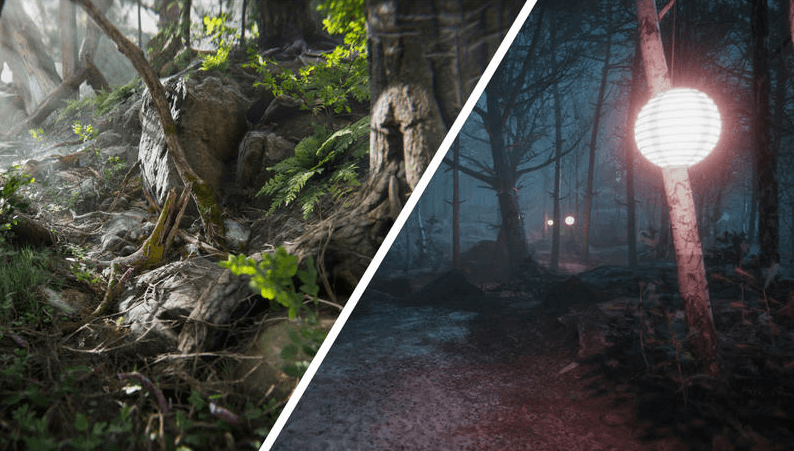

(Source)
Scenes and objects can also be pre-rendered, allowing users to interact in real-time with a version of an object or a scene that closely resembles a final rendering output. The process of rendering usually involves lots of computational power and requires time that depends on the complexity of a virtual scene that needs to be rendered.
Room-Scale (Tracking)
Room-scale tracking in virtual reality refers to the process of tracking user movements and actions within a space of a well-defined physical location such as a room or a hall. Room-scale tracking allows VR users to move freely within a defined space with tracking stations positioned strategically to accurately capture user movements within every part of that space.

https://cdn.circuitstream.com/uploads/2022/01/basestations_lifestyle.webm
Room-scale tracking helps VR users to experience virtual world immersion as their real-life movements will be accurately reflected in the virtual world.
S
Shading / Shaders
Shading is the implementation of depth in digital objects by applying the illumination parameter to pixels (in 2D) or polygon surfaces (3D). The shading model defines how to properly calculate the amount of light that reflects off every part of an object depending on light conditions and the object’s material. The model then dynamically changes involved parameters to ensure realistic light in a virtual scene.
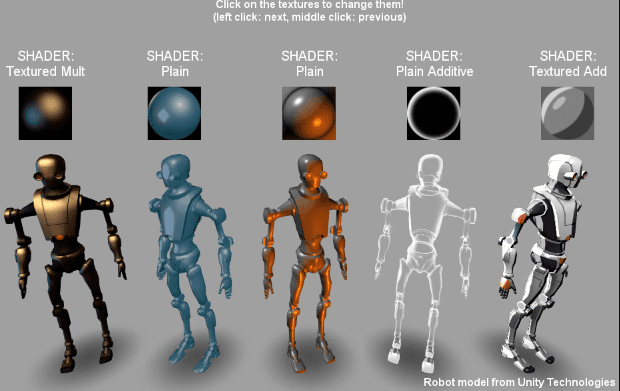
Although real-life shading is not necessary to evoke immersion in a virtual reality simulation, a believable lighting calculation vividly benefits the user’s experience, especially in simulations where real-life-like visual experience is a priority.
SLAM
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a problem of simultaneously mapping an unknown environment and tracking a user’s position within it. SLAM is essential in the field of robotics, virtual reality, augmented reality, autonomous transportation, and computer vision.

(Source)
There are several algorithms that solve the SLAM problem such as particle filter, Kalman filter, GraphSLAM, and covariance intersection. In virtual reality, SLAM is used to accurately represent the user’s physical environment for optimal comfort, safety, and navigation. In augmented reality, SLAM algorithms help build highly-detailed mapping and a user environment to accurately embed digital content within the real world.
Spatial Audio / 3D Audio
Spatial audio, or 3D audio, is a group of sound effects and technologies that manipulate digital audio output to create an illusion of dimensional sound for a listener. Devices that support spatial audio can create an effect of positional audio where a listener experiences a sound source above, below, or behind them.
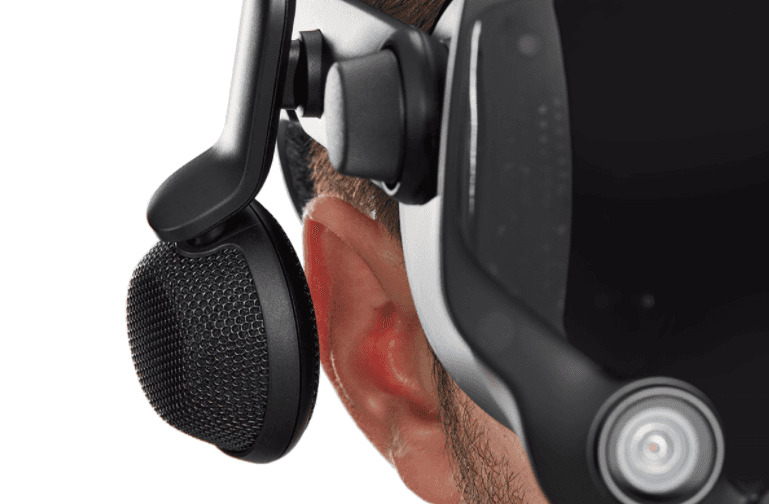

(Source)
An example of spatial audio in virtual reality is spatial audio systems built into VR headsets that allow users to experience sound in a virtual environment coming from various sources in a 3D space similar to the way we experience sound in real life.
T
Tethered / Untethered Headset
A tethered headset is a virtual reality headset that requires a computer for rendering and processing and a cable that connects a headset with a computer.
Examples of tethered headsets include Valve Index, Varjo VR 3, and Pimax 8K.
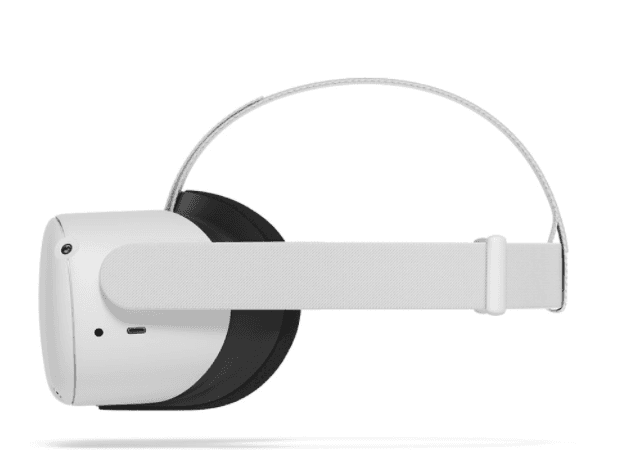
(Source)
Untethered headsets are self-sufficient and don’t require a computer to run a virtual simulation. Examples of headsets that provide tetherless experience: Oculus Quest 2 and HTC Vive Focus.
U
UI
User Interface (UI) refers to the combination of controls and design choices that define how users interact with a service, a system, or an object. Every virtual reality application has a user interface, and the smoother the user interface is designed, the more intuitive the interaction between a program and a user will be.
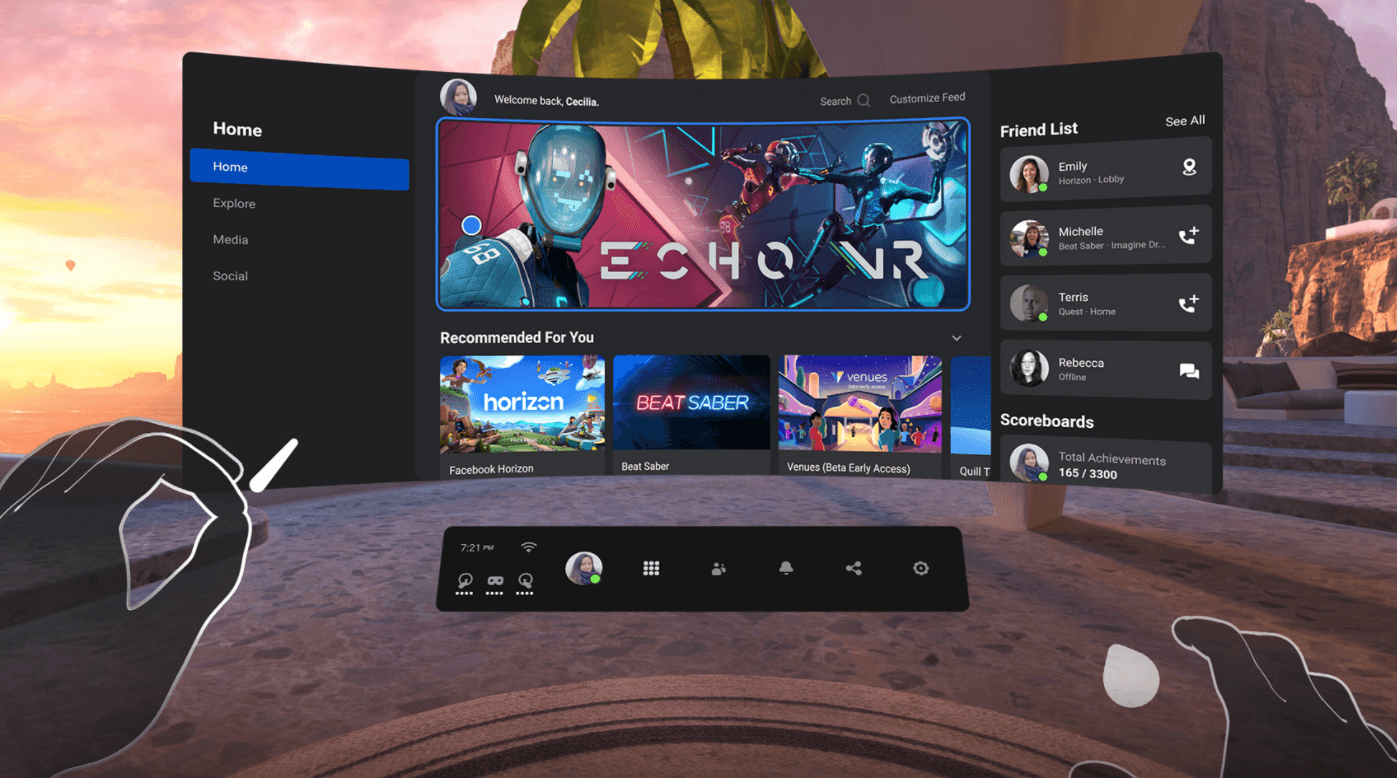
Source: Meta / Facebook
User interface designers rely on best usability practices, user testing, and best design practices to design and build user interfaces that allow new users to quickly get familiar with an unknown system or optimize the workflow of experienced users.
Unity Engine
Unity Engine (previously known as Unity 3D) is a cross-platform game and development engine used for creating desktop and mobile games, mobile applications, and virtual reality applications. The engine is written in C++ and C# languages and currently supports both free and commercial licensing. Unity 3D consists of a visual editor for creating and editing 2D and 3D scenes and an asset browser to manage in-game scripts and assets.
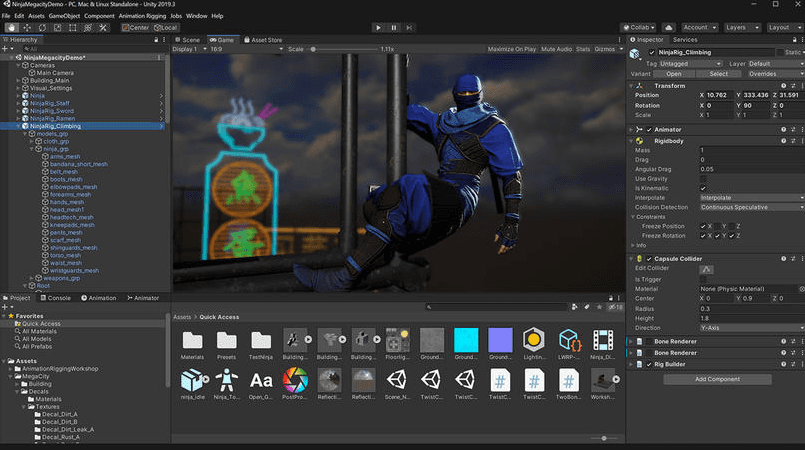
C# is the most commonly used language for creating Unity Engine applications followed by JavaScript and Boo. Unity hosts a large marketplace of 2D and 3D models, scripts, plugins, and gaming assets for development or prototyping. Apps developed with Unity can be released for 19 supported platforms including iOS, Android, Windows, Linux, and others. Unity supports the majority of modern virtual reality SDK.
Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine is a game development engine created by Epic Games in 1995. The current 4th iteration of the engine (UE4) features high-end graphics, a built-in codeless visual scripting system “blueprints”, an asset marketplace, photo-real ray tracing and lighting, and many others. Unreal Engine 4 is written in C++ and it’s the only supported development language.
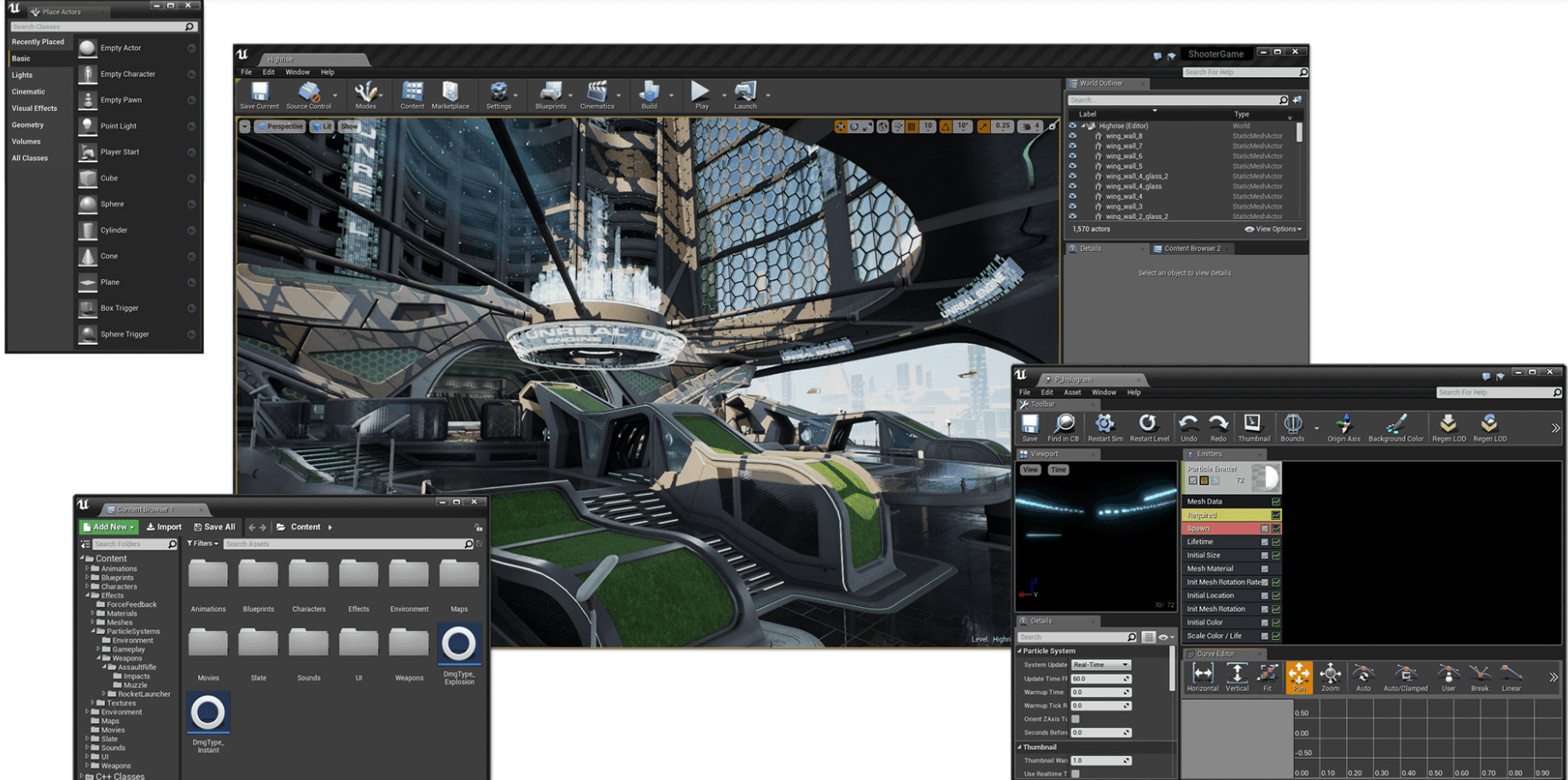
(Source)
UE 4 can be used for creating games, VR and XR applications, photo-realistic renderings and demo reels, animation sequences, and educational content.
The next version of the engine, Unreal Engine 5, is expected to be released in early 2022. The fifth version will feature a new virtualized micropolygon geometry system Nanite, fully dynamic global illumination, open-world collaboration, and a built-in rigging system for animation.
UX
User experience (UX) is an encompassing term that refers to reactions, experiences, and feedback that a user may have when interacting with a product, content, or service. The term was popularized in the 1990s and back then referred to the products that can evoke feelings of affection during usage. Nowadays the term largely applies to digital and technological products and their ability to inspire lasting positive reaction, loyalty, favorable feedback, and emotional attachment from a target user base.
User experience professionals utilize focus groups, surveys, and usability studies to define the level of user experience a particular product or system has and identify areas of improvement.
V
Vestibular System
Vestibular system is a human sensory system that contributes to a person’s balance, movement coordination, and orientation within a space. The human brain utilizes the vestibular system to understand a person’s position and kinematics at any given moment to keep balance and clear eye vision.
Even when in virtual reality simulation, a person still relies on the vestibular system to sustain balance and orientation in space. That’s why it’s crucial in VR simulations to ensure high-latency and accurate motion tracking to prevent vestibular system confusion that can lead to motion sickness, dizziness, and nausea.
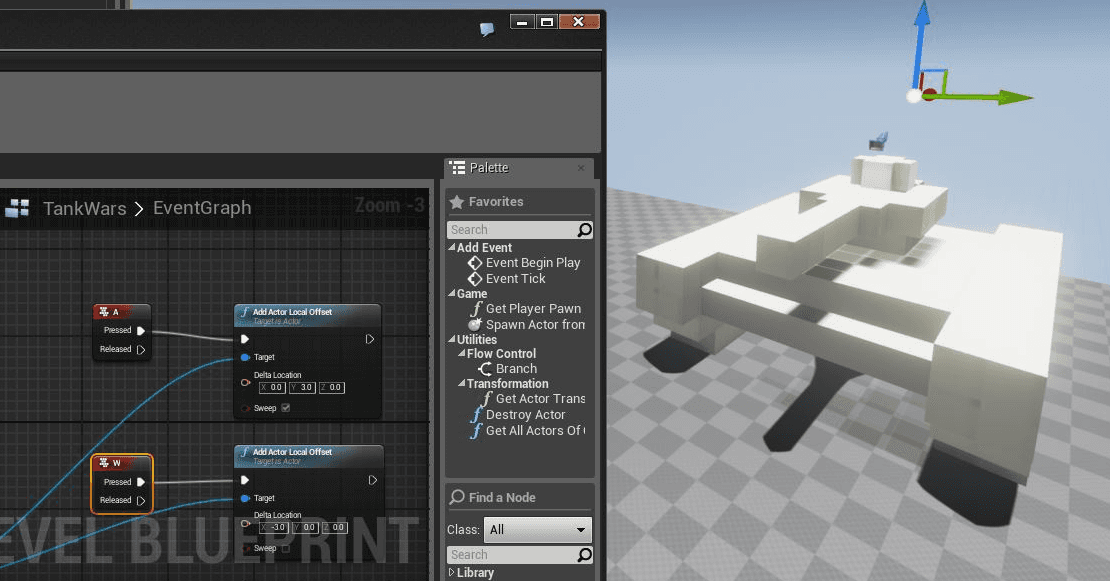
Visual Scripting
Visual scripting is a process of creating a game or application in a code-less visual environment commonly implemented with graphs, nodes, blueprints, and a graphical user interface.
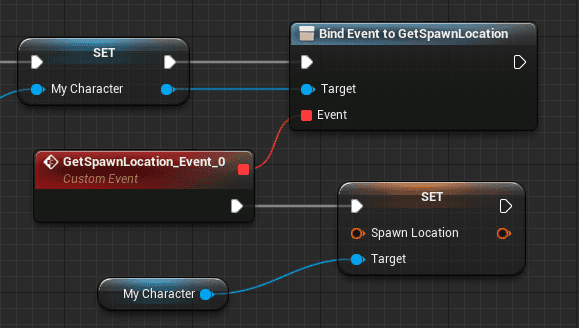
(Source)
Most popular gaming engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine offer visual scripting tools to help non-developers prototype and develop their applications without coding experience or facilitate collaborations between coding and non-coding departments within development companies.
Visual Studio
Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) and code editor developed by Microsoft. The software is commonly used by coding professionals for application, website, game, and web development and currently supports the most popular programming languages in each category.
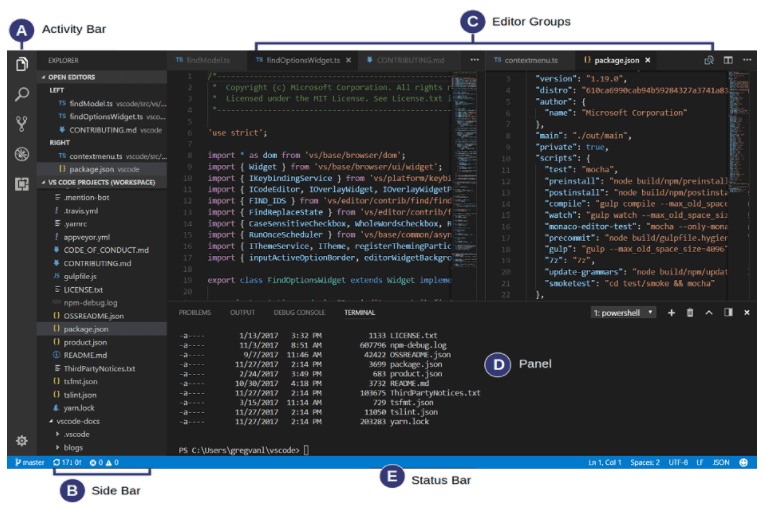
(Source)
Visual Studio offers completion tools, deployment management, debugging, and language-specific development features to optimize the developer’s workflow. Visual Studio is commonly used for developing C# and C++ scripts for Unity and Unreal Engine applications.
VR - Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is the creation of a simulated digital environment that a person can interact with through the use of immersive virtual reality devices. Users are typically engaged in a virtual reality world through a combination of visual experience, spatial audio, haptic feedback, and precise low-latency motion tracking.
(Source)
The most popular VR gateway device is a virtual reality headset with hand controllers, Additional devices used for creating an immersive virtual reality experience include haptic gloves, haptic costumes, full-body tracking costumes, virtual reality treadmills, and face tracking equipment.
WebXR
WebXR is an application programming interface (API) for transferring virtual reality and augmented reality applications to the web. WebXR is also capable of accepting input from VR control devices and mixed reality gamepads. WebXR manages rendering of the view of a 3D experience and detection of headset movements.
Wireframing
Wireframing is a process of creating a two or three-dimensional structure of an object or a scene in the form of an outlined contour. Wireframing is used to create a basic representation of an object without the need to spend additional time and resources on building a refined or finished version.
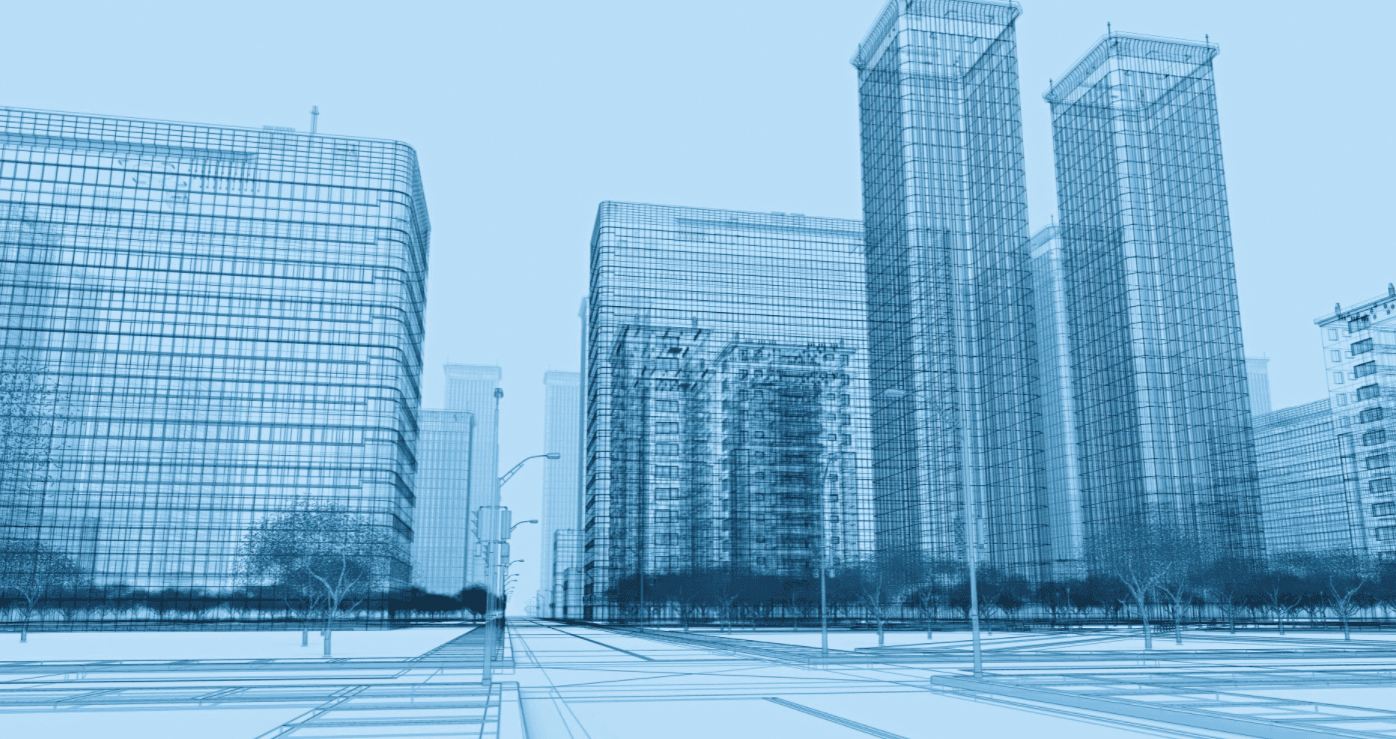

(Source)
Wireframes often serve as a starting point in the design process, an iterative brainstorming asset, or a way to gauge initial feedback from a client or a customer. In virtual reality, wireframes can also refer to simplified versions of 3D objects in a virtual space as a way to visualize the underlying structure of a 3D model.
X
XR - Extended Reality
Extended reality (XR) in an encompassing term for virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality applications, tools, and devices. XR technology enhances real-world user experience by either replacing the current user environment with a virtually generated one, augmenting the user real-world environment with a digital content, or a combination of both.

(Source)
XR technology is being actively developed and currently implemented in business, entertainment, education, and marketing spheres.